Clinical Trials In Indonesia

Over a million people are currently living with TB in Indonesia, making up more than 10% of the world’s TB burden. Of the estimated 32 000 new cases of drug-resistant TB in the country, only about a third of these cases were detected.

In a country with a high malaria burden, less than 1% of children with fever in malaria-endemic provinces were treated with appropriate anti-malarial drugs. [1]
About Indonesia
Indonesia is a country that consists of more than 17,000 islands, of which approximately 8000 are inhabited, with almost 250 million population, 300 languages making it the fourth most populous country.
- Indonesia has strong economic growth, an expanding middle class, and an urbanizing population
- It has a huge burden of infectious diseases and every year there are estimates of more than 1 million new TB cases, more than 1 million new malaria cases, and HIV epidemic growing at a fast rate
- In 2016 It was estimated that there are 48,000 new infections and in addition, there are many other infectious diseases that are still very common. [2]
Why clinical trials in Indonesia?
- Low operational costs compared to Western markets
- Enormous potential for recruiting study subjects
- Vast treatment-naive patient pool and Diversified population
- High incidence of infectious and chronic diseases in Asian countries
- Improved regulatory environment [3]
What is the regulatory body for clinical trials in Indonesia?
Clinical trials in Indonesia are regulated by the Indonesian Ministry of Health otherwise called Badan Pengawas Obat dan Makanan (BPOM). All clinical trials must comply with this decree to gain approval by the BPOM.
The clinical trials in Indonesia can be conducted directly by the sponsor or through a contract research organization (CRO), provided the CRO is based in Indonesia and complies with Good Clinical Trial Practice standards. [4]
What are the requirements to conduct Clinical Trials?
When applying to the BPOM for consent to initiate a clinical trial, the ensuing documents are essential:
- Clinical trial documents
- Clinical Trial Protocol
- Informed Consent
- Form Appendix
- Product documentation
Product Information
- Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
- Certificate of GMP
- Summary Batch Protocol
Other documents that may be requested include:
- GCP Certificate for Researchers
- Contract CRO (when using CRO)
- Insurance (if any)
- Certificate of Laboratory
Type of approval
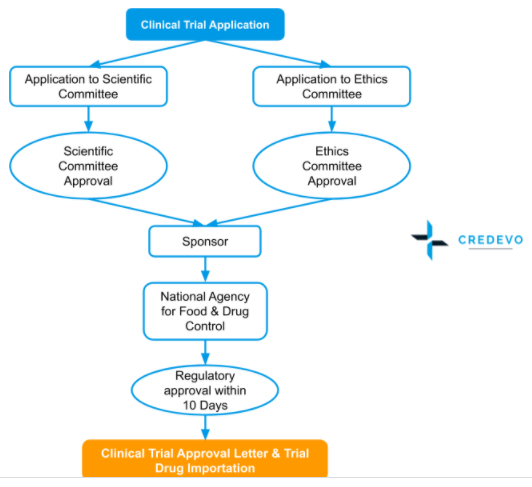
The type of clinical trial approval process is Sequential. Applicant or Sponsor can apply both to the Ethics committee and Scientific committee at once but the final approval for the trial will be only after the Ethics committee approval
Regulatory Approval Process
Pre-Approval
- The sponsor should get approval from the ethics committee before applying to the BPOM for permission to begin a clinical trial, which conducts the scientific and ethical review of the clinical trial documents.
- The sponsor can also apply simultaneously to the BPOM and the ethics committee.
- After the approval of the ethics committee, BPOM evaluates the clinical trial documents in consultation with a national team of clinical trial experts appointed by the agency and grants approval or rejection within twenty days of the submission.
- In some of the cases, the head of the agency may ask for additional data that must be promptly supplied to ensure that the process is completed in due time.
- If a clinical trial is approved, an approval letter is provided that is valid for two years.
Post-Approval
The head of the agency always has the authority to inspect the site before, during, or after the clinical trial and has the authority to terminate the project in case of any serious health risk.
In addition, the sponsor must inform the BPOM about:
- The progress of the clinical trial every six months.
- If any premature termination
- Any adverse effects during the trials
- Any changes in the trial procedure which were not mentioned earlier. [4]
Timeline for approval
The total timeline for the Regulatory process is 4-8 weeks and for the Ethics committee is about 4-6 weeks. [3]
Export of Biological samples
Material Transfer Agreement (MTA) is required for the export of biological materials in Indonesia to transport biological samples outside the country.
Recent changes in the Indonesian regulatory for Medical Devices
- Indonesia’s Ministry of Health (MoH) has enacted a new regulation 2017, concerning the Marketing Authorization of Medical Devices,
- The significant change noticed in this new regulation is the approval timeline. MoH has paved way for quicker registration processes in Indonesia by reducing the evaluation time. Besides, MoH will be no longer be issuing hard copy certificates.
- Herein the registration certificate will be issued in electronic form and can be printed by applicants through the Indonesian National Single Window portal, which can be accessed. [5]
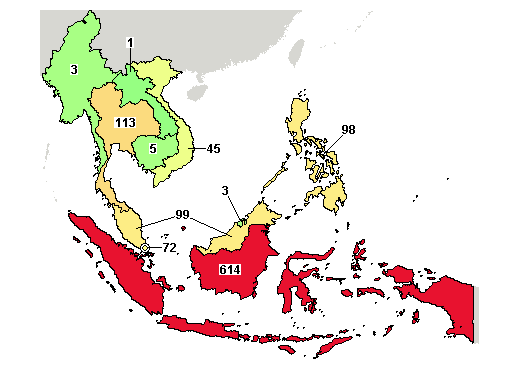
Clinical Trial numbers
A total of 614 trials were registered in Indonesia with 92 ongoing studies.
Major therapeutic areas for Clinical trials in Indonesia are
- Communicable & Infectious diseases
- Metabolic & Vascular diseases
- Respiratory disorders
- Lung & Heart diseases
Need Support in Indonesia or Have questions?
We’d love to help you conduct clinical trials in Indonesia.
Connect with experienced and resourceful sites, services providers, and experts in Indonesia.
Provide your details below.
Reference
- https://www.who.int/tdr/news/2017/indonesia-sets-research-priorities/en/
- https://khiri.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/Khiri-Indonesia_Destination-Information.pdf
- https://www.ijclinicaltrials.com/index.php/ijct/article/download/295/159
- https://www.phamax.ch/wp-content/uploads/bsk-pdf-manager/02082016040840AM_2.pdf
- http://www.qualtech.com.tw/en/about-qualtech/news1/976-indonesia-new-regulation-enacted-by-the-ministry-of-health-february-2018.html
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results/map?cntry=ID&map=SE
3 thoughts on “Clinical Trials In Indonesia”
Comments are closed.