Rare Diseases: Regulatory Incentives for Development of Orphan Drugs – JAPAN & AUSTRALIA

Regulatory agencies of various countries are providing benefits & regulatory incentives for orphan drugs such as faster approvals, fee concessions, and financial benefits, and many more. These incentives are to support and encourage pharma companies to work upon developing orphan drugs or medical devices for rare diseases.

The countries that provide regulatory incentives include the US, Europe, Japan, Australia, South Korea, and recently India. In the previous article, we have seen various regulatory incentives offered by the regulators of the USA and Europe.
Check out the first article in this series Rare Diseases: Regulatory Incentives for Development of Orphan Drugs – US & EU
In this article, we are going to go through the regulations in Japan and Australia for orphan drugs in rare diseases. The details on the incentives from China, South Korea, Russia, and India will be covered in the next article in this series.
Orphan drugs and rare diseases
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat orphan diseases or rare diseases. Because they are so rare, it would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. So to encourage development and research, a supportive legislative and regulatory framework (often known as orphan drug designation) is adopted for medicines for rare diseases in several countries.
Need regulatory support for your drug development in rare diseases?
Credevo provides complete services right from drug development strategy to market approval for drugs in rare diseases. Provide your details in the below form and talk to us now.
Regulatory incentives for orphan drugs in Japan & Australia
Along with FDA and EMA, many other regulators like PMDA and TGA are providing various incentives for researchers in orphan drugs
Orphan drug regulations in Japan
A disease is considered to be rare if it occurs in less than 1 in 2,500 people in Japan.
The MHLW (Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare) makes orphan drug designation and approval decisions on a case-by-case basis.
Criteria for orphan designation status in Japan
- The number of patients who may use the drug or medical device should be less than 50 000 in Japan.
- The development plan should be appropriate and establish a theoretical rationale for the product for the target disease.
- The drugs or medical devices indicated for the treatment of serious diseases, including difficult-to-treat disease.
- In addition, they must be drugs or medical devices for which high medical needs are satisfying one of the following criteria.
- There is no appropriate alternative drug/medical device or treatment.
- Expect high efficacy or safety compared with existing products.
Regulatory incentives for orphan drugs in Japan
Financial benefits
- Subsidy payment: Orphan drug/medical device applicants can receive subsidies through the National Institute of Biomedical Innovation (NIBIO), as this helps to reduce the financial burden of product development and R & D expenses.
- Lower fee: Applicant can avail lower user fee categories for consultation with PMDA for orphan designated drugs.
- Tax benefit: Applicant can claim 12% of study expenses for orphan drug/medical devices incurred during the NIBIO subsidy payment period (not including subsidies granted by NIBIO) as a tax credit.
Regulatory benefits
- Guidance and consultation: Orphan drug/medical device applicants can receive guidance and consultation from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW), the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), and NIBIO on research and development activities. PMDA provides a priority consultation system for designated orphan drug/medical devices.
- Priority review: Designated orphan drugs and medical devices will be subject to expedited review for marketing authorization to ensure that they are supplied to clinical settings at the earliest possible. Categories of lower user fees are applicable to review for marketing authorization of designated orphan drugs.
Marketing benefits
- Extension of re-examination period: The re-examination period can be extended up to 10 years for drugs and up to 7 years for medical devices, after orphan drug/medical device designation and approval.
Orphan designation process in Japan
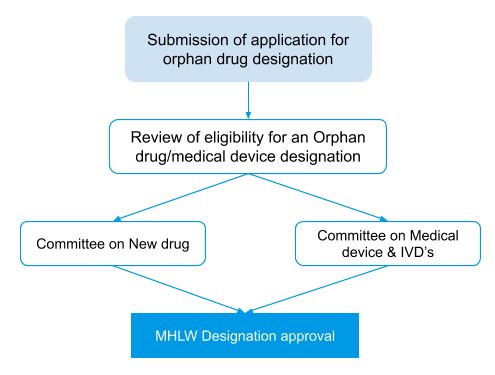
Read more about Rare Diseases: Clinical Trials & Drug Development
Orphan drug regulations in Australia
A disease is said to be rare if it occurs in less than 1 in 2,000 in Australia.
Criteria for orphan designation status in Australia
- If the medicine is intended to treat the condition which affects fewer than 5 in 10,000 individuals in Australia when the application is made.
- If it is not likely to be financially viable for the sponsor to market the medicine in Australia unless each fee referred to in paragraph 45(12)(c) of the regulations were waived in relation to the medicine.
Regulatory incentives for orphan drugs in Australia
Financial benefits
- Fee waiver: The sponsor needs to pay the determination application fee if applying for orphan drug designation, at the same time as an application for priority determination or provisional determination. This fee is reimbursed if orphan drug designation is approved.
- Evaluation fee: Evaluation fees are waived for prescription medicine registration applications if a related orphan designation is in force.
- Orhan Designation Extension: There is no fee for applications to extend orphan drug designation.
- Orphan Designation Extension: There are no fee charges for applications to extend orphan drug designation.
Regulatory benefits
- Provide a consistent and transparent process for assessment against the eligibility criteria.
Marketing benefits
- Market exclusivity: Orphan-designated medicines which fulfill the criteria for the designation are granted 5 years of market exclusivity protection.
Understand how to manage the challenges faced in Clinical Trial Logistics for Rare Disease Clinical Trials
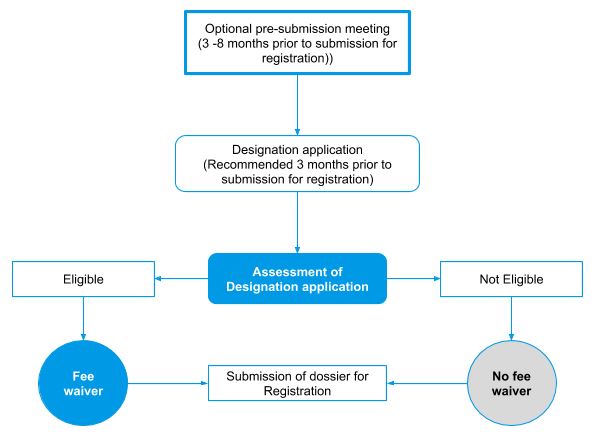
Orphan designation process in Australia
Overview of regulatory incentives for orphan drugs in Japan & Australia
| Criteria | Japan | Australia |
| Legal framework Regulation | Orphan Drug Regulation (1993) | Orphan Drug Policy (1998) |
| Administrative authorities involved | Orphan Drug Division (ODD) | TGA |
| Prevalence of the disease (per 10,000 individuals), justifying the orphan status | 4 | 11 |
| Marketing exclusivity | 10 Years | 10 Years |
| Tax credit or benefit | 6% for any type of study + limited to 10% of the company’s corporation tax | No |
| Grants for research | No | National Grants |
| Reconsideration of applications for orphan designation | Yes | Every 6 months |
| Technical assistance for the elaboration of the application file | Yes | No |
| Accelerated marketing procedure | Yes | Yes |
Are you looking for regulatory support for your drug development in rare diseases?
Talk to us today. Provide details of your requirements and we will connect with you.
Way forward
Utilize these incentives to your advantage in the development of medicines for rare diseases, or orphan drugs, as they are commonly known.
Interested in knowing more about these benefits from other countries?
Find out in the next articles in this series about incentives and support mechanisms for rare diseases in
4 thoughts on “Rare Diseases: Regulatory Incentives for Development of Orphan Drugs – JAPAN & AUSTRALIA”
Comments are closed.