Rare Diseases: Regulatory Incentives for Development of Orphan Drugs – The United States & Europe

Many regulatory agencies across the world are offering incentives for the development of orphan drugs for rare diseases. These incentives include financial benefits, faster approvals, less stringent clinical data requirements, and many more. The countries that are offering the regulatory incentives for orphan drugs include the US, Europe, Japan, Australia, South Korea, Brazil, and most recently, India.

These incentives have been so supportive and convincingly helpful that they have boosted drug development across the world.
Orphan drug market
Worldwide orphan drug sales are forecast to grow at a CAGR of 12.3% from 2019 to 2024, which is approximately double the rate forecast for the non-orphan drug market. By 2024, orphan drug markets are expected to reach $242bn and capture one-fifth of worldwide prescription sales.
Orphan drugs and rare diseases
An orphan drug
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat orphan diseases or rare diseases. Because they are so rare, and would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. It’s a designation given based on some considerations.
A rare disease
Rare diseases are defined a bit differently across various countries, though the basic consideration remains the same, i.e. the number of patients is very small.
Let’s first discuss the United States and European regulatory scenarios and benefits.
Review the next articles in this series for incentives and benefits in other countries for rare disease drug development, rare disease clinical trials, and orphan drug approvals for marketing.
Orphan drug regulations in the United States
In the United States, a drug or biologic may be designated as an orphan drug if it is to prevent, treat, or diagnose a disease/condition that occurs in less than 200,000 patients.
Criteria for orphan designation status in the United States
For a drug to get an orphan drug status requires to fulfil the following criteria
- A drug has not been approved earlier.
- An agent with a new orphan indication.
- A drug proved clinically superior over previously approved drugs of the same category.
Orphan designation process flow in the USA
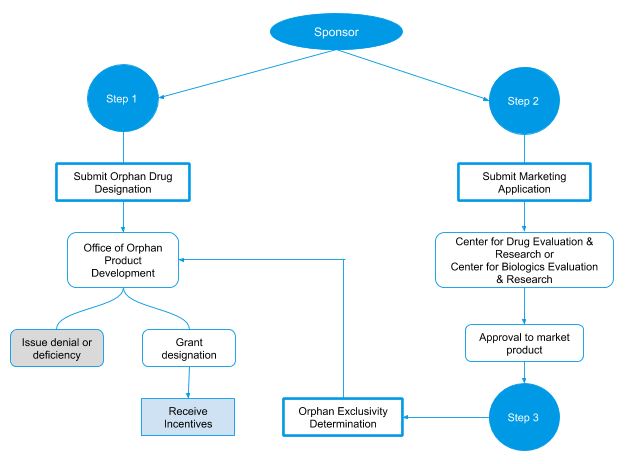
Incentives for orphan drugs in the USA
The US-FDA provides various benefits for research in orphan drugs for rare diseases, lets check one by one
Financial benefits
- Tax incentives: The Orphan Drug Tax Credit (ODTC): The sponsors, after obtaining orphan drug designation, can collect tax credits for expenses incurred while conducting a clinical trial.
- User fee: Orphan drug products are exempt from the usual new drug application or user fees charged by the FDA.
Regulatory benefits
- The Rare Pediatric Disease Priority Review Voucher Program says that a sponsor, who receives approval for a drug or biologic for a “rare pediatric disease” may qualify for a voucher. This voucher can be redeemed to receive a priority review of a subsequent marketing application for a different product.
- The drug approval process will be eligible to go through a fast-track procedure for evaluation by the FDA.
- The sponsor receives assistance and guidance from the FDA in the design of an overall drug development plan.
Clinical development benefits
- Orphan Product Grant program provides funding for clinical testing of new therapies to treat and/or diagnose rare diseases and this lowers the drug development cost.
Read more about Rare Diseases: Clinical Trials & Drug Development
Marketing benefits
- Market exclusivity: A drug approved by the FDA for a specific indication gets 7 years of marketing exclusivity. The market exclusivity for an FDA-approved new chemical entity is typically five years. For orphan drugs, the FDA will not award market authorization for a generic drug for the rare disease for seven years post-approval. However, this incentive is superior to traditional IP patent protection and a substantial incentive.
- The orphan drug can be available to patients before gaining market approval. Treatment Investigational New Drug (t-IND) may be obtained under specific conditions, in some cases of compassionate use, such as
- The drug is intended for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening disease.
- No alternative drug or treatment must be available.
- The product is in the process of clinical trials and an active phase of marketing approval.
Understand how to manage the challenges faced in Clinical Trial Logistics for Rare Disease Clinical Trials
Medical device
- The Humanitarian Use Device (HUD) program designates that the medical devices. The medical devices, that are intended to benefit patients in the treatment or diagnosis of a disease or condition that affects or is manifested in not more than 8,000 individuals in the United States per year as eligible for Humanitarian Device Exemption.
Orphan drug regulations in Europe
An orphan drug in Europe
A disease is considered to be rare if it occurs in fewer than 5 in 10,000 people.
The EU offers several incentives to encourage companies in the research and development of medicines for rare diseases that otherwise would not be developed. Companies can apply for orphan designation for medicine to access these incentives which meet certain criteria proposed by the EMA.
Do you know the primary challenge in rare disease clinical trials and, a ready solution available to handle it?
Criteria for orphan designation status
- The disease must not affect more than 5 in 10,000 people across the EU.
- The medicine must treat, prevent, or diagnose a disease that is life-threatening or chronically debilitating, or it is unlikely that the medicine will generate sufficient returns to justify the investment for its development.
- No satisfactory method of diagnosis, prevention, or treatment exists, or if such a method already exists, the medicine must be of significant additional benefit to those affected by the condition.
Orphan designation process flow in Europe
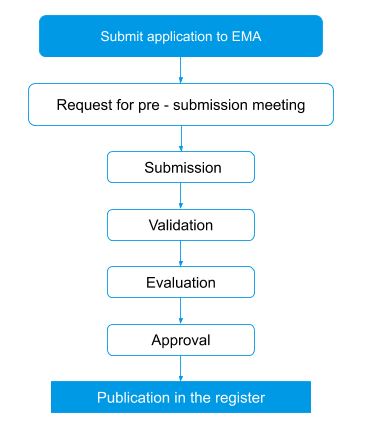
Incentives for orphan drugs in Europe
Europe’s EMA provides various incentives and benefits for orphan drug researchers, and these are,
Financial benefits
- Research & Development: During research and development of orphan medicine’s, the company can benefit from incentives such as
- Scientific advice on study protocols,
- Various fee reductions, and
- Access to EU grants.
- Small companies: The Agency encourages companies developing orphan medicines to check if they can be classified as a micro, small or medium-sized enterprise (SME). Such companies can benefit from further incentives, including administrative and procedural assistance from the agency’s SME office and fee reductions.
- Companies who apply for designated orphan medicines can pay reduced fees for regulatory activities such as
- Protocol assistance,
- Marketing-authorization applications,
- Inspections before authorization,
- Applications for changes to marketing authorizations made after approval, and
- Reduced annual fees.
- Grants: The Agency does not offer research grants for sponsors of orphan medicines, but the European Commission and other sources may provide funding.
Regulatory benefits
- Pediatric medicines: Medicines authorized across the EU with the results of studies from a pediatric investigation plan included in the product information are eligible for an extension of their supplementary protection certificate. For designated orphan medicines, the incentive is an additional two years of market exclusivity.
- Centralized authorization procedure: All orphan designated medicines are assessed for marketing authorization centrally in the European Union. This allows companies to make a single application to the European Medicines Agency, so results in a single opinion and a single decision from the European Commission, which is valid in all EU Member States. Sponsors may also have access via orphan designation to conditional approval, which is conducted under the centralized procedure.
- Global benefits: The two authorities, EMA and FDA have also developed common procedures for applying for orphan designation and for submitting annual reports on the status of the development of designated orphan medicines.
Marketing benefits
- Designated orphan medicines are eligible for conditional marketing authorization. In some cases, designated orphan medicines may be allowed to be administered to patients under compassionate use, which is a treatment option that allows the use of an unauthorized medicine outside a clinical study.
- 10 years of market exclusivity protection: A 10 years of market exclusivity protection is granted for the medicines that eventually make it to the market, and for which it can be demonstrated that they fulfill the criteria for the designation.
- This period of protection can be extended by two years for medicines that also have complied with an agreed pediatric investigation plan granted at the time of review of the orphan medicine designation.
Global orphan drug sales are estimated to reach $262B by 2024; nearly double of that registered in 2018 with $138B. These statistics show the growing interest in rare diseases and the development of orphan drugs.
Comparison of US & EU regulatory incentives
| Criteria | USA | Europe |
| Legal framework Regulation | Orphan Drug Act (1983) | Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products (COMP) |
| Administrative authorities involved | Office of Orphan Product Development (OOPD) | Committee of Orphan Medicinal Products (COMP) |
| Prevalence of the disease (per 10,000 individuals), justifying the orphan status | 7.5 | 5 |
| Marketing exclusivity | 7 Years | 10 Years |
| Tax credit or benefit | 50% for clinical studies | Managed by the member states |
| Grants for research | programs of NH and others | FP6′ + national measures |
| Reconsideration of applications for orphan designation | No | Every year |
| Technical assistance for the elaboration of the application file | Yes | Yes |
| Accelerated marketing procedure | Yes | Yes – Centralized procedure |
Are you looking for regulatory support for your drug development in rare diseases?
Talk to us today. Provide details of your requirements and we will connect with you.
Way forward
Utilize these incentives to your advantage in the development of medicines for rare diseases, or orphan drugs, as they are commonly known.
Interested in knowing more about these benefits from other countries?
Find out in the next articles in this series about incentives and support mechanisms for rare diseases in
References
- https://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/Education_AboutOrphanDrugs.php?lng=EN&stapage=ST_EDUCATION_EDUCATION_ABOUTORPHANDRUGS_USA
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2631478/
- https://www.fda.gov/industry/developing-products-rare-diseases-conditions
- https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/research-development/orphan-designation/orphan-incentives
4 thoughts on “Rare Diseases: Regulatory Incentives for Development of Orphan Drugs – The United States & Europe”
Comments are closed.