Marketing Authorization Procedure For Pharmaceuticals In Europe

Most of the processes to approve drugs in the EU are similar to those of the FDA, such as getting pre-authorization for use of the drug in clinical trials. After clinical trials, FDA drug approvals follow a centralized path, whereas European approval can occur through 4 different paths, depending on the nature of the drug, timeline, and the preference of the manufacturer.

Before a medicinal product can be placed into the market for sale and supply. the product must be the subject of a valid Marketing Authorisation (MA) for human or veterinary use from a regulatory authority.
What is the regulatory body in Europe?
Pharmaceutical regulatory systems in the EU comprise a decentralized body called the European Medicines Agency (EMA), Heads of Medicines Agencies (HMA), National Competent Authorities (NCAs) and European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines (EDQM). and collection of rules and regulations governing medicinal products in the EU is Eudralex.
The European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA) was established in London, in the year 1995, to coordinate the European Union (EU) member states for evaluating and controlling the medicinal products for both human and veterinary use
- The European medicines regulatory system is based on a network of around 50 regulatory authorities from the 31 EEA countries (28 EU Member States plus Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway)
- EMA is responsible for the scientific evaluation, essentially of innovative and high-technology medicines developed by pharmaceutical companies for use in the EU.
EMA has various committees for various categories of medicinal products
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP)
- Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC)
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CMVP)
- Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products (COMP)
- Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC)
- Committee for Advanced Therapies (CAT)
- Paediatric Committee (PDCO)
For a medicinal product to seek market authorization in Europe, the manufacturer or sponsor shall choose a pathway from four different pathways based upon the type of medicinal substance, and requirements such as a number of countries chosen for marketing, timeline, etc.
What are the various procedures available for marketing approval of medicinal products in EUROPE?
A sponsor has several options to seek market approval for a new drug in Europe: a National Authorization Procedure, a Decentralized Procedure, a Mutual Recognition Procedure, and a Centralized Procedure.
Based on the drug category, number of countries planning to market the drug, timeline of approval and the budget sponsor can go this one of the pathways described below
National authorization procedure
This procedure is for the sponsor who is planning to market the drug in one of the European countries
- Within Europe, each country has its own procedures for authorizing market approval for a new drug.
- The National procedure is specific to each country within the EU has its own systems for authorizing a marketing application for a new drug. The sponsor can visit the regulatory agency website for each country in which he is interested to obtain market approval.
- To obtain marketing authorization in a country, the application must be submitted to the Competent Authority of that Member State in its own language.
- The timeline for this procedure is 210 Days. (without any stop clock queries)
Advantages of this procedure
- The fees are affordable even for small firms
- It saves on translation cost to English or Regional languages
- It provides a base for Mutual recognition Procedure, where if sponsor plans to extend to other countries for marketing
Medicines that cannot follow this procedure
Some of the medicines don’t fall under this category and is regulated by EMA and the following categories are
- Orphans Medicinal Product
- All Biotechnology Based Product
- Specified Aids and Cancer Medicines
- Specified Antiviral Medicines
- Specified Medicines for Neurodegenerative Disorder including diabetes and Specified Medicines for Autoimmune Disorders
Centralized procedure
A single marketing authorization allows the sponsor to market the medicine and make it available to patients and healthcare professionals throughout Europe in the “Centralized procedure” and is granted by the European Commission following the scientific assessment of the application by the European Medicines Agency.
- The centralized process is controlled through the EMA and issues a single license valid in all EU member states.
- An identical application for marketing authorization is simultaneously submitted to the competent authorities of the Reference Member State – RMS and of the Concerned Member States – CMS.
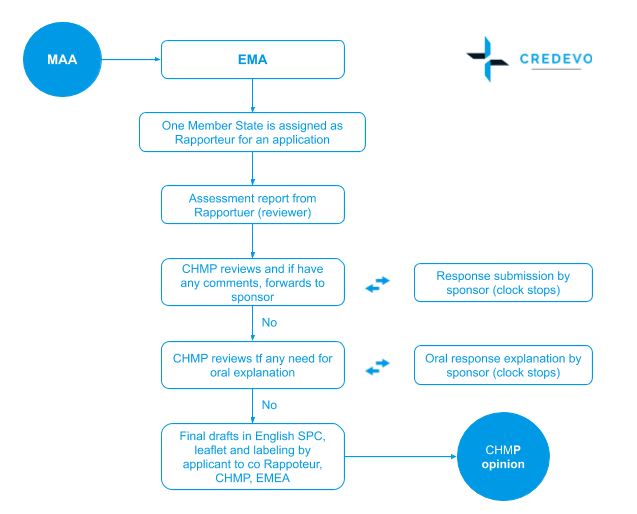
- One Member State is assigned Rapporteur (reviewer) for an application and takes the lead in the evaluation process of the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use – CHMP
- At the end of the process, the draft assessment report, Supplementary Protection Certificate – SPC, labeling and package leaflet, as proposed by the Reference Member State, are approved.
- Under the centralized procedure, a company may only obtain one marketing authorization per medicinal product. However, in specific cases, a company may apply for duplicate marketing authorization.
Products that are eligible for review under the centralized procedure must meet the following criteria:
- Biologic drugs developed by recombinant technology, controlled expression of genes coding for biologically active proteins in prokaryotes and eukaryotes including transformed mammalian cells, and hybridoma and monoclonal antibody methods
- Orphan medicinal products or drugs for rare diseases
- Medicinal products that contain new active substances for indications like AIDS, cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, autoimmune disorders.
The centralized procedure was mandatory only for biotechnology medicines initially, but later on, the mandatory scope of the centralized procedure has been gradually extended and included orphan drugs or medicines for rare diseases, human medicines that contain a new active substance, advanced therapy medicines and medicines that are intended for the treatment of AIDS, cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, auto-immune and other immune dysfunctions, and viral diseases.
Procedure
Pre-submission
- A sponsor must notify the EMA of their intention to submit a market authorization application and the month of submission at least seven months prior to submitting the application.
- This includes
- A document outlining the reasons the sponsor believes the application should fall under the centralized procedure.
- The EMA will consider the presubmission and notify the sponsor of its decision regarding acceptance of the MAA.
Submission
- Companies wishing to market a medicinal product submit their application directly to the European Medicines Agency (EMA)
- The EMA‘s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) conducts a scientific assessment of the application and gives a recommendation on whether the medicine should be authorized or not.
- The scientific review process consists of periods of evaluation and periods during which the clock is stopped in order to give the applicant time to resolve any issues identified during the evaluation.
- A positive opinion is accompanied along with a draft summary of the product’s characteristics, the package leaflet, and the proposed text for the packaging.
- The time limit for the evaluation procedure is 210 days, subject to extensions if additional questions need to be addressed.
- Within 15 days of the adoption, the EMA will forward its opinion to the European Commission to start the decision-making phase and within 15 days a draft implementing decision is sent by the Commission to the Standing Committee on Medicinal Products for Human Use.which allows for its scrutiny by EU countries.
- The Commission’s Secretariat-General then notifies the decision to the sponsor or marketing authorization holder and the decision is published in the Union Register.
Post authorization
- Before a medicine is marketed, it will be subject to pricing negotiations and a review of its cost-effectiveness. This is carried out at the national level by the Member States to determine reimbursement criteria.
Process flow
Product name
- The name for the drug product shall be the same in all countries within Europe, besides where it violates trademark rules.
- The sponsor shall submit the proposed name in advance, usually 4 to 6 months, and not more than 12 months of the marketing authorization application.
Pricing and reimbursement
After granting marketing authorization, decisions about price and reimbursement take place at the level of each Member State considering the potential role and use of the medicine in the context of the national health system of that country.
Validity
- A National Marketing Authorisations are valid for five years.
- Applications for renewal must be made to the EMA at least six months before this five-year period expires and this review takes into consideration of any learning obtained about the product from the experience gained by its use since it was first authorized,
Advantage of the centralized procedure
- The main advantage of this procedure is, It requires a single market approval procedure and if authorized, results in the authorization valid in all EU countries and the same product information available in all EU languages.
Decentralized Procedure
Sponsors can apply for market approval in more than one EU state for products simultaneously, that have not yet been authorized in any EU state and do not fall under the mandatory centralized process.
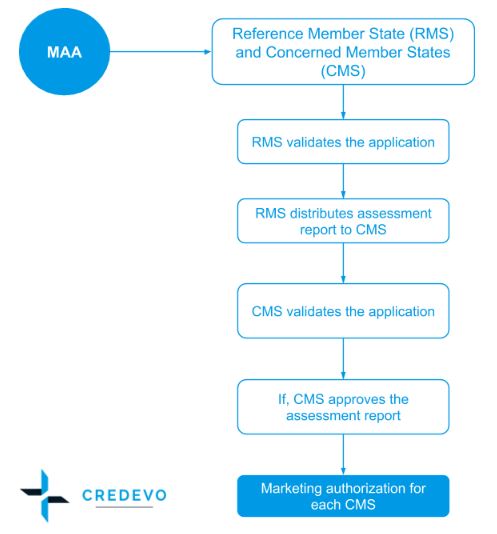
- The applicant chooses one country as the Reference Member State – (RMS) when making its application for marketing authorization. Chosen reference Member State then prepares a draft assessment report that is submitted to the other Member States where approval is sought for their simultaneous consideration and approval.
- The RMS forwards a preliminary Assessment Report on the dossier to the Concerned Member States – CMS(s) and the applicant within 70 days
- Allowing the other Member States access to this assessment at an early stage, any issues and concerns can be dealt with quickly without any delay
- The CMS(s) are asked to give their comments on the proposed national prescription status and to inform the RMS.
- The RMS will forward all comments to the applicant and stops the clock if necessary until the applicant prepares a response document.
- The RMS prepares a Draft Assessment Report on day 120 and may close the procedure if a consensus has been reached between the CMS(s) and the RMS.
- Or, the CMS(s) has 90 more days to approve the Draft Assessment Report and other documents.
- The competent authorities of the RMS and the CMS(s) adopt a decision within 30 days after acknowledgment of their agreement to the Assessment Report and other documents.
- Finally, at the end of the Decentralized Procedure with a positive agreement, a national marketing authorization will be issued in the RMS and each of the CMS(s).
Process flow
Advantages of this procedure
- The sponsor or manufacturer receives identical marketing authorization for its medicinal product in all chosen member states at the same time.
- It is possible to launch a product on the market in several different EU countries simultaneously, thus reducing the associated launch costs and potentially creating a strong brand and presence for the product in the EU from day one.
- The sponsor who seeks generic medicines prefers this decentralized procedure often
Mutual Recognition Procedure
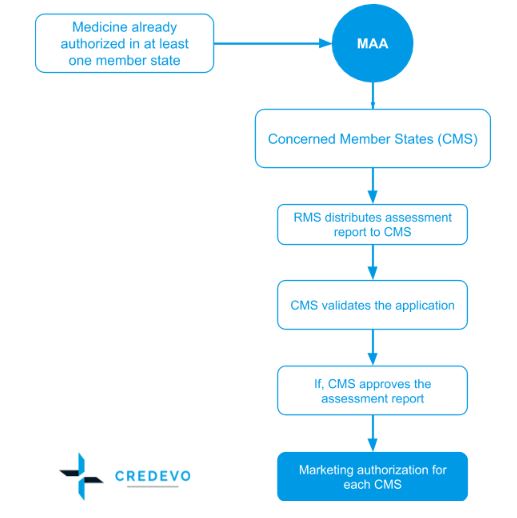
In this procedure, the medicinal products, approved in one European country and seek further marketing authorizations from other EU countries, who, rather than conducting their own review, agree to recognize the decision of the first country.
- The sponsor is required to make an application only once for initial registration. The same application with some regional changes is accepted by another member country.
- The first Member State that reviews the application is called the Reference Member State – RMS and notifies other states, called ‘Concerned Member States – CMS.
- The concerned Member States may suspend their own evaluations to await assessment by the Reference Member State.
- The decision of the Reference Member State is forwarded to the Concerned Member States and If the Concerned Member States reject mutual recognition, the matter is referred to as the CHMP of the EMA for arbitration.
- The EMA forwards its opinion to the European Commission, which makes the final decision. Altogether, the decision process may take up to 300 days if there is no objection and 600 days when objections are raised.
- This process may consume a time period of 390 days.
Process flow
What is the Union Register?
The Union Register lists all medicinal products for human use, veterinary use, and orphan medicinal products that have obtained marketing authorization by the Commission through the centralized procedure. The register also includes information such as suspended or withdrawn or refused for authorization products, medicinal products that were refused nationally, etc.
Manufacturer regulations
Manufacturers listed in the application of a medicine to be marketed in the EU are inspected by an EU competent authority. This includes manufacturers located outside the EU unless a mutual recognition agreement (MRA) is in place between the European Union and the country of manufacture.
For a medicinal product, manufactured outside the EU, to be imported into the EU, it needs to undergo full analytical testing in the EU unless a mutual recognition agreement (MRA) is in place between the EU and the exporting country.
An active pharmaceutical ingredient needs to be accompanied by a written confirmation issued by the competent authority of the country where it is produced and confirming that the good manufacturing practice (GMP) applied is at least equivalent to the recognized EU GMP standards.
Are you planning to market your medicinal product in EUROPE?
Talk to us today. Provide preliminary details below and we will help you achieve a successful registration in EUROPE. Credevo can be your strategic partner to make a successful submission in a timely manner. You will get a complete overview of the regulatory framework, process overview, and timelines associated with submissions.
References
- https://ec.europa.eu/health/authorisation-procedures-decentralised_en
- https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register_en
- https://ec.europa.eu/health/authorisation-procedures-centralised_en
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2452302X16300638
- https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/leaflet/european-regulatory-system-medicines-european-medicines-agency-consistent-approach-medicines_en.pdf