How To Get Started With Your Clinical Trials In Australia – Regulatory And Site Perspectives

Australia has the world’s best researchers and health professionals, a world-class research infrastructure, and high standards for clinical trial conduct, which leads to quality, increased speed, and high confidence in the results.
Note: This article was last updated in April, 2023.

They have quality research facilities, an efficient ethical and regulatory framework, a diverse participant recruitment pool, research tax incentives, and flexibility in conducting research.
Top 5 reasons to conduct clinical trials in Australia
There are several reasons why Australia is an attractive location to conduct clinical trials:
- Fastest route to start clinical trials: Australia offers one of the fastest and most efficient regulatory paths to initiate clinical trials, particularly through the CTN scheme.
- Highly Skilled Workforce: Australia has a highly skilled and educated workforce with a strong focus on medical research. The country boasts of world-renowned researchers and clinicians, making it a hub for innovative medical research.
- Robust Regulatory Framework: Australia has a robust regulatory framework for clinical trials, ensuring the safety of trial participants and the integrity of trial data. The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) is responsible for regulating therapeutic goods, including medical devices and drugs.
- Well-established Infrastructure: Australia has well-established infrastructure and facilities for clinical trials. This includes state-of-the-art hospitals, research institutions, and clinical research organizations (CROs) that can provide high-quality services and support for clinical trials.
- Access to Patient Populations: Australia has a diverse patient population, making it an ideal location for clinical trials that require a range of patient demographics. Additionally, Australia has a universal healthcare system, which means that patients have access to healthcare services regardless of their ability to pay.
- Competitive Cost Structure: The cost of conducting clinical trials in Australia is generally competitive when compared to other developed countries such as the United States and Western Europe. Additionally, the Australian government offers financial incentives to companies conducting research and development in the country.
- Favorable Time Zone: Australia’s time zone is favorable for conducting clinical trials that require collaboration with the Asia-Pacific region or other parts of the world. The country is well-positioned to work with countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea, which are major players in the global pharmaceutical industry.
Along with these reasons, questions may arise for those interested in Australia for conducting clinical trials, which include
- What are the regulatory processes (hurdles?), and
- How can we find the sites to conduct clinical trials there?
In these articles, let’s try to address these questions.
Regulatory for Clinical trials in Australia
Regulatory authority for conducting clinical trials in Australia
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) is the regulatory body in Australia. The TGA regulates the quality, supply, and advertising of medicines, pathology devices, medical devices, blood products, and many other therapeutics.
Australian sponsor
You must have an Australian sponsor to conduct a clinical trial in Australia.
The sponsor may be an,
- Individuals (medical practitioners),
- A body or organization (hospitals, area health services, non-government organizations), or
- A company (pharmaceutical companies, CROs).
TGA would deal directly with the Australian sponsor on all matters relating to the trial.
Human Research Ethics Review (HREC)
- The ethics committee must have notified its existence to the Australian Health Ethics Committee (AHEC) of the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) and provided assurances that it is operating within its guidelines.
- Ethics committees in Australia provide a combined ethical and scientific review process,
- HRECs have a pivotal role in clinical research in Australia because they undertake the key responsibilities of clinical trial approval and oversight
- HRECs operates under the auspices of the Australian Health Ethics Committee.
- Additionally, public hospitals are required to undertake a research governance step in the form of a site-specific assessment (SSA) for each project.
- Therefore, for public sites, HREC and SSA are required for a clinical trial to commence.
- The institution or organization where the trial will be conducted will give the final go-ahead for conducting the trial at the site, having taken into account advice given by the HREC.
- CTN research projects must not start at a site until the research project and investigational site have been notified to the TGA and the appropriate notification fee paid.
- It is preferable to wait for the TGA to confirm receipt of the CTN before recruitment commences.
Research Governance Office (RGO) approvals
- According to AUS-43 and the G-TrialsSOP, all participating institutions must also authorize any research in accordance with their research governance frameworks, including site-specific assessments (SSAs) for public health institutions. The SSA and ethics review (incorporating scientific review) may occur in parallel.
- If the sponsor chooses private sites to conduct clinical trials may not require RGO approval. if the sponsor chooses to include public sites will require RGO approval.
Where to submit the trial application?
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) does not assess some therapeutic products. But we can list them on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG) for general marketing. There are two main processes for submitting those clinical trial ideas.
- Clinical Trial Notification (CTN) or
- Clinical Trial Approval scheme (CTA) scheme (formerly known as Clinical Trial Exemption (CTX) schemes.
Need support for your clinical trials in Australia?
Are you looking for regulatory support in various stages of drug development? Write to us at [email protected] or provide your requirement details in the form below
Clinical Trial Notification (CTN)
A Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC) should conduct the necessary scientific and ethical examination in this situation and notify the TGA afterward.
Note: Under the Australian regulatory framework for biologicals certain Class 4 biologicals are not able to be supplied under the CTN Scheme and must be submitted under the CTA scheme.
Clinical Trial Approval scheme (CTA)
Under this plan, the TGA is directly involved in checking the clinical trial’s scientific data. The TGA should approve the proposed trial program before it can begin.
Clinical studies that don’t use “unapproved” medicinal products are exempt from CTN or CTA regulations. If a product is an “unapproved” therapeutic good, the Australian clinical trial sponsor is responsible for making that determination.
Approval time for clinical trials in Australia
Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC) review takes 1-3 months (however, it depends upon the institution), and CTN review takes about 7–14 days.
The process for getting permission to operate a clinical trial
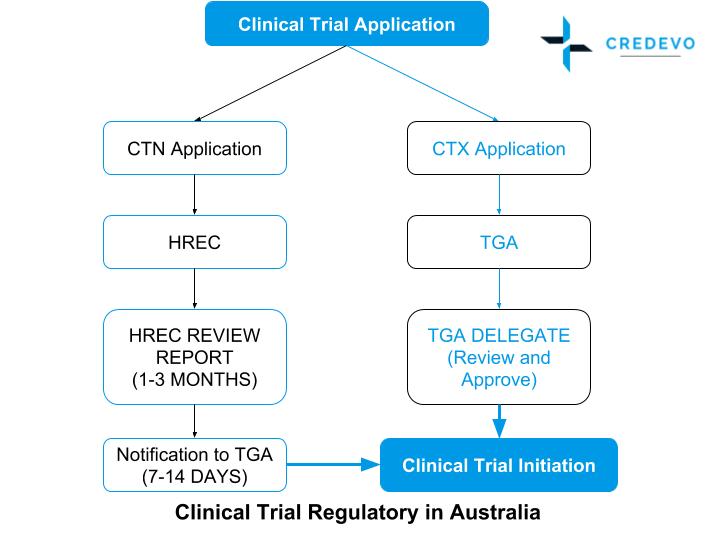
Legends: CTN- Clinical trial Notification, CTX- Clinical trial Exemption, TGA-Therapeutic Goods Administration, HREC-Human Research Ethics Committee
NOTE: HERC Review time depends upon the institution
Now let’s understand the CTN & CTA schemes in details.
Clinical Trial Notification scheme (CTN)
The CTN Scheme is a notification procedure that involves the following:
- The Australian clinical trial sponsor should inform the TGA before using an unapproved medicine. It is necessary to submit the notification form online and pay the associated fee.
- The TGA may send a formal request for specific information regarding the products listed on the CTN form to the clinical trial sponsor.
- The TGA does not examine any data relevant to the clinical trial at the time of submission.
- The Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC) evaluates,
- The trial protocol
- The scientific validity of the trial design
- The risk and benefits of the therapeutic product
- The acceptability of the trial procedure from an ethical standpoint
The HREC is in charge of monitoring the trial’s execution as well.
- The “Approving Authority,” the institution or organization where you conduct the clinical trial, grants final approval after taking the HREC’s recommendations.
- The sponsor is in charge of confirming all necessary approvals are in place before providing the clinical trial with the “unapproved” therapeutic products.
CTN submission process
- You can submit a clinical trial notification (CTN), online through the TGA Business Services (TBS) website.
- If the organization already has online access to TBS, it will have a client ID without online access to TBS.
- You should nominate the administrator via the organization details form to gain access to TBS.
- CTN applies to new and existing organizations with a TGA client identification number (client ID).
- You should apply for a new client ID if it doesn’t already have one.
Clinical Trial Approval scheme (CTA) – forms
There are two forms, each reflecting separate processes (Parts), that must be submitted to TGA by the sponsor.
- Part 1 constitutes the formal CTA application. It must be completed by the sponsor of the trial and submitted to TGA with data for evaluation.
- Part 2 is used to notify the commencement of each new trial conducted under the CTA as well as new sites in ongoing CTA trials. The Part 2 form must be submitted within 28 days of the commencement of the supply of goods under the CTA.
Fee structure for clinical trials in Australia
Here are the fees/charges for various categories.
| Category | Fee |
|---|---|
| Prescription medicine, biological, and other listed and registered therapeutic goods CTN. | $345 AUD |
| Prescription medicine CTX for 30-day evaluation. | $1,665 AUD |
| Prescription medicine CTX for 50-day evaluation | 20,800 AUD |
| Biological CTX | $25,200 AUD |
Applications for clinical trials under the CTX scheme cost more than notifications under the CTN scheme because of the increased work needed to evaluate the CTX application data.
Applications for clinical trials under the CTX scheme cost more than notifications under the CTN.
One can find more information about the on the TGA website.
Medical device trials
The clinical trial regulatory process for devices is essentially similar to that for medicines. Often, the protocol is sent in by the sponsor/principal investigator(s) with the CTN notification form, and in such instances comments are provided on the document by the medical advisory staff. CTX applications for medical devices are rare.
Top benefits of conducting clinical trials in Australia
Quality research and facilities
for its highly trained clinical workforce and the high-quality data produced by its experienced, trained (and accredited) research teams.
Efficient ethics and regulatory framework
Research proposals are submitted directly to Australian Human Research Ethics Committees (HRECs) which assume the primary review responsibility for ethical and scientific review.
The usual review cycle takes only 4 to 8 weeks and is based on the submission of a protocol, investigator brochure and if required, an independent toxicology report.
The diverse participant recruitment pool
Australia has an informed and willing population of potential trial participants, resulting in a higher level of research participation than would be expected from a population of its size.
Investment incentives
The Australian Government’s generous Research & Development (R&D) Tax Incentive encourages more industry investment in R&D.
The Incentive provides businesses investing in eligible R&D with generous tax offsets:
- A 45 percent refundable R&D tax offset (equivalent to 45c per $1 of eligible R&D) for companies with an aggregated annual turnover of less than A$20 million; and
- A 40 percent non-refundable R&D tax offset (equivalent to 40c per $1 of eligible R&D) for all other eligible companies.
Flexibility
Companies conducting clinical trials in Australia do not require the US FDA Investigational New Drug (IND) application approval.
Data output from studies carried out in Australia meets global standards and can be used to support international regulatory applications, including the US FDA IND submission. This makes the process more efficient, flexible yet ethical.
Australia offers a lot to all kinds of drug / medical device / biotech companies in terms of market expansion. It’s always interesting to consider Australia in your global strategy.
Need Support in Australia or Have questions?
We’d love to help you conduct clinical trials in Australia. Provide your details below to connect with us and explore our expert services in Australia.