Japan: Medical Device Approval Process

The Japanese medical device market stands second after the USA. The global data expects the Japanese medical device market to grow from $54.5 billion in 2018 to $74.7 billion in 2025, at a compound annual growth rate of 4.6% (CAGR).
Note: This article was updated in September, 2022.

Top reasons to choose Japan for your medical device market
The Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (MHLW) took several steps to improve the transparency of the review system in order to accomplish a quick and easy device approval process. As a result, the approval process is equivalent to or faster than in the North American and European markets.
Here are a few reasons to select Japan as your medical device market.
- Increase in the aging population,
- An increase in the number of patients with chronic and lifestyle diseases, and
- The Japanese government took several measures in order to improve the reach of new innovative medical devices to patients.
Japan Medical Device Regulations & Approval Process
Regulatory for Medical Device in Japan
The Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (MHLW) is the primary regulatory body in Japan that creates and implements safety standards for medical devices and drugs. On the other hand, the Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau is in charge of pharmaceutical and medical device regulatory policies.
While the tasks of MHLW include
- Register manufacturers,
- Grant licenses (MAH etc.),
- Validate ministerial ordinances, guidelines, and industry standards,
- The final release of medical device authorizations, and
- Monitor the PMDA.
The Pharmaceutical Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) is an independent administrative agency that works with the MHLW in order to ensure both the safety and quality of medical devices and drugs in Japan and a technical arm of the MHLW.
Due to such responsibility, the Pharmaceutical Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) performs
- The review and approval of the medical device,
- Conducts QMS/GLP/GCP inspections,
- Inspections of manufacturers for compliance with GMP, and
- Collects and analyzes adverse event reports.
Since Medical Devices undergo regulatory approvals based on the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Law (PMDL) in order to register and enter the Japanese market, Medical device manufacturers need to comply with the various regulatory requirements that apply and need to follow a process for authorization.
Click here to know about the drug approval process in Japan
How foreign manufacturer can market their medical device in Japan?
Foreign manufacturers intending to manufacture drugs, quasi-drugs, Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs), or medical devices overseas and planning to import into Japan need to register with the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (MHLW). And this process is known as Foreign Manufacturer Registration (FMR), and this process is also known as Toroku.
Previously FMR was known as Foreign Manufacturer Accreditation (FMA).
Since the FMR is an extra layer of the process necessary for foreign manufacturers with medical device registration, the foreign manufacturers need first obtain the FMR and then obtain device registration.
Need support to register your medical device in Japan?
Credevo offers expertise in drug products & medical device registration, clinical trial regulations processing, and many more services in Japan. Connect with us to check them out now!
Can manufacturers submit foreign clinical trial data?
Yes, manufacturers can submit foreign clinical data based on the clinical studies conducted outside of Japan for Marketing approval for medical devices in Japan. PMDA accepts and reviews foreign clinical data on medical devices.
Requirements and approval process for medical devices in Japan
All foreign companies who intend to register their medical device with the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (MHLW) should follow nine approval steps.
Steps to register your medical device in Japan
- Categorize the medical device: Identify the class of your device as per the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act (PMD Act) and Japanese Medical Device Nomenclature (JMDN) codes.
- Establish QMS requirements: Based on the device class, determine the QMS requirement.
- Appoint an MAH or D-MAH: Class I device require MAH, while all other class devices require MAH or D-MAH who control your registration.
- Obtain necessary authorizations and licenses,
- Foreign manufacturers shall submit Foreign Manufacturer Registration (FMR),
- Authorization procedure selection,
- Submit the authorization documents,
- Request a QMS Inspection, and
- Plan the post-market period.
The process and timeline to register a medical device depends on the class to which it belongs. So, it is crucial to understand the class of medical devices before initiating any registration process.
Classification of medical devices in Japan
- Class I devices
- The devices come under Class I when the risk to patients is almost negligible in the event of a malfunction (ex. X-ray films).
- These classes of devices are also known as General Devices.
- Class II devices
- The devices come under Class II when the risk to patients is relatively low in the event of a malfunction (ex. MRI, digestive catheters, etc.).
- These devices are also known as Controlled Devices.
- Class III devices
- The devices come under Class III when the risk to patients is relatively high in the event of a malfunction (ex. artificial bones, dialyzer, etc.).
- These devices are also known as Specially Controlled Devices.
- Class IV devices
- These devices are highly invasive with fatal risks to patients (ex. pacemaker, artificial heart valves, etc.).
- These devices are also known as Specially Controlled Devices.
Quality Management System (QMS)
PMDA conducts on-site and document-based inspections of manufacturing sites in Japan or overseas. It is to ascertain whether their manufacturing facilities and manufacturing and quality controls comply with standards such as the Quality Management System (QMS) and whether manufacturing sites have a system for manufacturing products of adequate quality.
Regulatory process for Class I Devices
The approval process of Class I devices is also known as Todokede.
Some of the requirements for the approval of Class I device include
- The device category,
- Name (generic/proprietary),
- Intended use of the device,
- Device shape,
- Structure, etc.
The MAH needs to file a notification for approval, and since these devices are of low risk, they may not require the assessment by the PMDA.
The sponsor shall apply for the Quality Management System (QMS) that complies with the PMD Act with the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare (MHLW). The sponsor needs to register the manufacturing facilities too.
Regulatory for Class II Devices
The approval process of Class II devices is also known as Ninsho.
The necessary documents to register Class II devices include details of intended use, the proprietary name of the device, device shape, device structure, direction for use, method of manufacturing, storage conditions, shelf life, etc.
- The MAH needs to initiate the application with a notarized body.
- In a few cases, some Class II devices may require review by both the regulatory bodies, the PMDA and MHLW.
- The foreign manufacturers may require an extra step for approval because, with device approval, the foreign manufacturer needs to obtain the FMA.
- This class of medical devices requires the QMS.
Since the approval timeline depends on the completeness of the application, the timeline varies from four to nine months.
Regulatory for Class III & Class IV Devices
The approval process of Class III and Class IV devices is also known as Shonin.
The documents to make the application include general requirements, such as medical device category, intended use, efficacy risk analysis data, clinical data, etc. Along with this, it also requires a Summary of Technical Documentation (STED).
- Since the risk associated with the Class III and Class IV devices are the same, the application remains almost the same with a few differences. Based on the risk, in a few cases, this review process is also applied to Class II controlled devices.
- The sponsor needs to apply to the PMDA, and the PMDA conducts a QMS conformity assessment inspection at the manufacturing site.
Since the approval depends on factors such as the completeness of the application, QMS, and risk associated with the device, the timeline for approval varies accordingly.
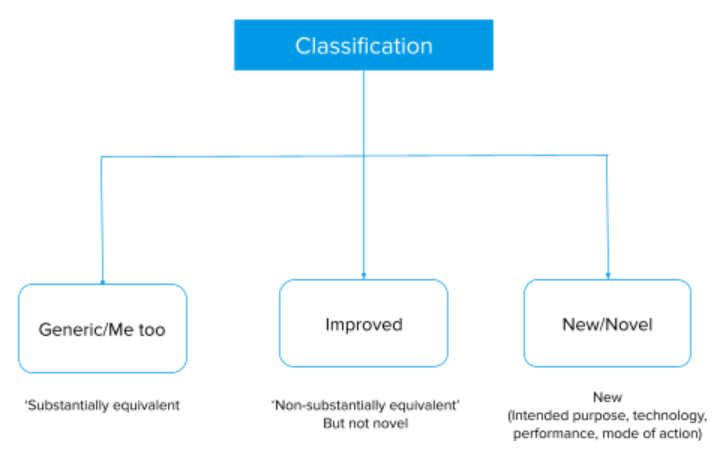
Medical Devices application categories
Apart from the class, medical devices are also considered based on the device criteria as below.
- New medical devices (require clinical trial data)
- New improved medical devices (require clinical trial data)
- Improved medical devices (does not require clinical trial data)
- Me-too medical devices (these does not require clinical trial data)
- Me-too medical devices (these does not require clinical trial data and compliance with approval standards).
Japan Medical Device Nomenclature (JMDN) codes
- The Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (MHLW) maintains a database of generic device descriptions associated with Japan Medical Device Nomenclature (JMDN) codes.
- This JMDN system is similar to the Global Medical Device Nomenclature (GMDN) system or the US FDA nomenclature system.
- If the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (MHLW) database does not contain the device code, then the product needs to undergo a new registration pathway based on the device class.
Expiration, and renewal of device registration
- Medical device registration doesn’t expire, but, the sponsor should renew the QMS certificates every five years.
- In order to avoid delays, the sponsor should initiate the renewal process six months before the expiration.
- Pre-Market certification applications may also be subject to annual surveillance audits by the authority.
Do you need support or have queries on the medical device registration?
Credevo offers a wide range of regulatory services in Japan. Select one of the following options to connect with us.
Get the report on the medical device registration process in Japan.
Note: This report will be charged @ $2880.
Do you have a query? Just ask experts at Credevo.
Note: “Ask Credevo Expert” will be charged @ $50 / inquiry. Any inquiry requiring more than 30 min of the expert’s time will incur additional charges.
Looking for a quotation? Just provide relevant info and we will send you the details.