Drug Approval Regulatory & Process In The United States – I

The United States represents the largest continental pharma market worldwide and holds around 45% global market. The pharmaceutical market in the United States was expected to increase from $354bn in 2015 to $497bn by 2020. The FDA is the main regulatory body that handles drug approval in the United States.

Though markets like China and India have shown a massive leap in the pharma market, the United States and Europe are still the key players in the pharmaceutical industry.
The United States has the world’s most stringent standards for approving drugs, and drug approval standards are considered the benchmark by many regulators worldwide.
Which is the regulatory body for drug approval in the USA?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for protecting and promoting public health.
The Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is a division of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that monitors most drugs as defined in the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act.
FDA approval process begins only after the submission of the Investigational New Drug (IND) application.
Who can submit IND, NDA & NDA 505(b)(2) drug applications?
- The applicant, or the applicant’s attorney, agent, or authorized official must sign the NDA.
- If the person signing the NDA does not reside or conduct business within the United States, the NDA is required to contain the name and address of, and be countersigned by, an attorney, agent, or an authorized official who resides or maintains a place of business within the United States.
Need support for your drug registration in the USA?
Credevo offers expertise in drug product registration, clinical trial regulations, and many more services in the USA. Complete the form below to connect with us!
The approval process for Investigational New Drug (IND)
If the results prove safe in the preclinical trials, the sponsor can submit an Investigational New Drug (IND) application with the FDA to start clinical trials in humans. The sponsor is responsible for the submission of the IND application.
A Pre-IND assessment can be organized with the FDA to deliberate multiple issues such as:
- The design of animal research, which is required to lend support to clinical studies.
- The intended protocol for conducting the clinical trial.
- The chemistry, manufacturing, and control of the investigational drug.
Requirements for IND application
The requirements for the IND include 1571, 1572, 364 FDA forms, protocols, chemistry, manufacturing, and control information, pharmacology, and toxicology information, etc.
Approval process for IND
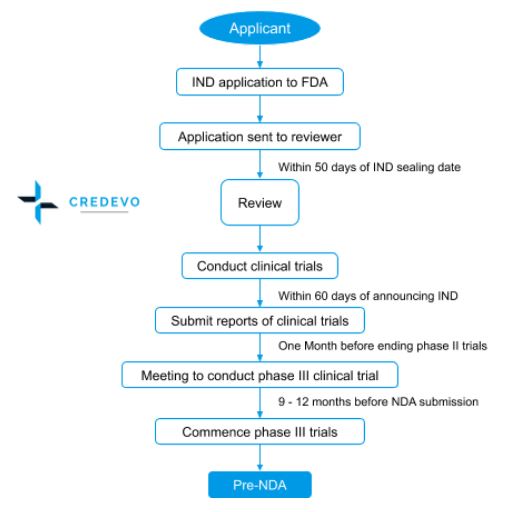
- An applicant with all the required information applies to FDA.
- On receiving the application, FDA forwards it to the review team.
- Within 30 days after the IND sealing date, the review team provides its positive or no response where the sponsor can start clinical trials.
- Within 60 days from announcing the IND, the sponsor shall submit the reports of clinical trials.
- The sponsor shall conduct a meeting one month before ending phase II trials.
- After the completion of phase III trials successfully the sponsor shall initiate pre-NDA from 9 – 12 months before NDA submission.
Timeline for IND approval
Generally, the FDA approves within two years. However, this timeline may be from several months to years due to several reasons.
The approval process for New Drug Application (NDA)
A New Drug Application (NDA) can be filed only when the drug successfully passes all three phases of clinical trials and comprises all animal and human data, analyses data, the pharmacokinetics of the drug, and its manufacturing and anticipated label.
The preclinical, clinical reports, and risk-benefit analysis are studied at the Centre for Drug Evaluation and Research
Requirements for NDA submission
The requirements for the NDA submission require two copies of application
- Archival copy and
- Review copy.
The archival copy serves as a reference source for FDA reviewers to locate information not contained in the review copy, and each technical section is separately bound in each folder in the review copy.
New Drug Application (NDA) approval process
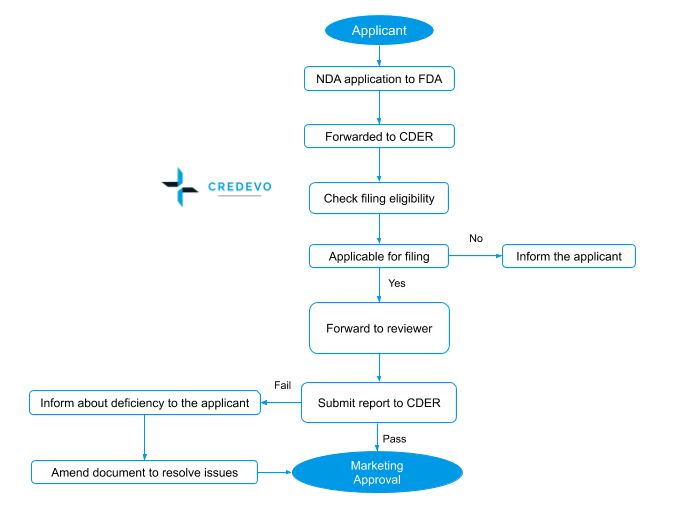
- The process starts with a Pre-NDA meeting and this meeting addresses the submission of the NDA including issues such as format and content, etc.
- Pre-NDA meeting is followed by the NDA submission and review.
- The FDA has 60 days to decide whether to accept the file to review.
- FDA forwards this file to CDER for review and CDER will evaluate the eligibility for filing. If found eligible accepts the application and forwards it to the FDA reviewer team.
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) conducts inspections of regulated facilities to determine a firm’s compliance with applicable laws and regulations, such as the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act and related Acts.
- Within 180 days the reviewer team submits the report to CDER.
- If the review result is positive, FDA issues marketing authorization to the sponsor.
What is NDA 505(b)(2)?
A 505(b)(2) application is one for which one or more of the investigations relied upon by the applicant for approval which was not conducted by or for the applicant and for which the applicant has not obtained a right of reference or use from the person by or for whom the investigations were conducted.
An example of 505(b)(2) applications include an application for a change in the route of administration, such as a change from an intravenous to an intrathecal route.
New chemical entity (NCE)/New Molecular Entity (NME)
A sponsor can submit a 505(b)(2) application for an NCE (New Chemical Entity) when some part of the data necessary for approval is from studies not conducted by or for the applicant and to which the applicant has not obtained a right of reference.
For an NCE, this data is likely to be derived from published studies, rather than the FDA’s previous finding of the safety and effectiveness of a drug.
Changes to previously approved drugs
- An application may rely on the agency’s finding of safety and effectiveness of the previously approved product, along with the information needed to support the change from the approved product.
- The intent of section 505(b)(2) is to encourage innovation without creating duplicate work and reflects the same principle as the 505(j) application.
Approval procedure for NDA 505(b)(2)
The approval process follows same as NDA approval
Timeline for NDA 505(b)(2) approval
Once the applicant applies, FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) expects to review and act on at least 90 percent of NDAs for standard drugs no later than ten months.
What is the regulatory for generic drugs/ANDA?
The Office of Generic Drugs (OGD) ensures, through a scientific and regulatory process, that the generic drugs are safe, effective, and high-quality.
FDA-approved generic drugs account for about 90 percent of prescriptions filled in the United States.
Types of Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) approval
There are two types of ANDA approval
- Full Approval: all valid patents and exclusivities for the reference listed drug (RLD) are expired or any legal issues that may block approval of the ANDA are settled.
- Tentative Approval means that FDA has concluded that a drug product has met all required quality, safety, and efficacy standards, but because of existing patents and/or exclusivity rights, it cannot yet be marketed in the United States.
Procedure for Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) approval
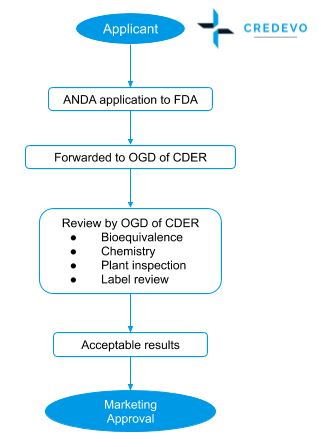
- The sponsor shall apply ANDA to FDA under section 505(j).
- A regulatory team reviews the file to determine whether the application is sufficiently complete to permit a substantive review.
- Acceptance/Refuse to Receive (RTR) letter is issued based on the completeness of the Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA).
- If all the information submitted by the applicant is acceptable, the OGD of CDER issues market approval.
Timeline for ANDA approval
The initial review cycle may be adjusted by mutual agreement between the FDA and an applicant as the result of a major amendment.
Patent and exclusivity
Patent and exclusivity in 505(b)(2) application
- A 505(b)(2) application may itself be granted 3 years of Hatch-Waxman exclusivity if one or more of the clinical investigations, other than BA/BE studies was essential to approval of the application and is conducted or sponsored by the applicant.
- The 505(b)(2) application may also be granted for 5 years of exclusivity if it is for a new chemical entity.
Do you need support or have queries on drug registration requirements in the USA?
Credevo offers a wide range of drug development and regulatory services in the USA.
References
- https://www.fda.gov/drugs/types-applications/new-drug-application-nda
- https://www.fda.gov/drugs/types-applications/abbreviated-new-drug-application-anda
- https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=314.50
- https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Investigational-New-Drug-Applications-Prepared-and-Submitted-by-Sponsor-Investigators.pdf
- https://www.turacoz.com/regulations-of-drug-approval-in-united-states-european-union-and-canada/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2452302X1600036X
- http://tech.snmjournals.org/content/18/4/236.full.pdf
- https://drug-dev.com/fda-update-the-fdas-new-drug-approval-process-development-premarket-applications/
- https://repository.upenn.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1025&context=ace