South Korea – Clinical Trials Regulatory Process

With a population of over 51 million people, South Korea offers a diverse patient population with a range of medical conditions, making it an ideal location for conducting clinical trials with a broad range of participants. Additionally, the country has a well-developed healthcare system and skilled workforce, making it an attractive location for clinical research. South Korea has a long history of conducting global clinical trials than most other Asian countries including, Japan.
This article was last updated in April 2023.

Why South Korea for your clinical trials?
According to ClinicalTrials.gov, as of September 2021, there were approximately 7,000 active clinical trials being conducted in South Korea. This indicates that South Korea is a popular destination for clinical trials, and many global pharmaceutical and biotech companies are conducting clinical trials in the country.
The types of clinical trials being conducted in South Korea are diverse and cover various therapeutic areas, including
- oncology,
- cardiology,
- neurology, and
- infectious diseases, among others.
Top 5 Advantages of conducting clinical trials in South Korea
- It is a clinical trial destination with world-class medical infrastructure and a highly educated, relatively wealthy, and healthy population.
- Well-resourced hospitals in South Korea generally conduct trials and maintain adherence due to a high degree of professionalism and a culture of deep respect between patients and physicians.
- The South Korean government has introduced several electronic resources such as the clinical trials e-registration system that opens immediately after IND approval and a self-registration system for Contract Research Organizations (CROs).
- The country’s patient recruitment, retention, and compliance rates are higher than in most Western countries and are comparable with other emerging Asian countries.
- All Phases of studies are conducted in South Korea, but, the majority of studies are Phase III trials.
All of these factors contribute to a country with one of the shortest startup times in Asia.
Need support for conducting your clinical trials in South Korea?
Credevo offers expertise in drug product registration, clinical trial regulations, and many more services in South Korea. Provide the details of your requirements in the form below to connect with us.
Along with these above facts, there are also some challenges while conducting clinical trials in South Korea
Top 3 Challenges with clinical trials in South Korea
- Patient Recruitment: Despite having a large patient population, patient recruitment can be challenging in South Korea, particularly for trials involving rare diseases or specific patient populations. This is because patients may be hesitant to participate in clinical trials due to cultural beliefs, language barriers, or concerns about privacy.
- Competition from Other Countries: South Korea faces stiff competition from other countries, such as China and Japan, which are also popular destinations for clinical trials. This competition can lead to challenges in attracting sponsors and investment for clinical trials.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Although South Korea has a well-established regulatory framework for clinical trials, navigating the regulatory environment can be challenging for researchers and sponsors. The process of obtaining regulatory approval for clinical trials in South Korea can be time-consuming and complex, leading to delays and additional costs.
Here is where credevo can help you in conducting your clinical trial in South Korea. Contact us at [email protected] or fill out the form below to get support for clinical trials in South Korea.
Clinical trial regulatory process in South Korea
- The Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS), formerly known as the Korea Food & Drug Administration (KFDA), is the main regulatory body for drugs, medical devices, food, and cosmetic products.
- The MFDS provides pre-investigational new drug consultation services.
- To conduct a clinical trial in South Korea, the sponsor must obtain institutional review board (IRB) approval.
- The sponsor should submit a clinical trial application with the appropriate supporting documents, all of which should be translated into Korean.
- The IRB approval process can take 1-2 months in Korea.
Requirements to obtain approval for clinical trial initiation
Clinical Trials for medical devices in Korea
- Foreign companies must first prepare a clinical investigation plan and provide documents proving that their manufacturing facility meets GMP standards to submit a clinical trial application for a medical device in Korea.
- If the device is used to treat life-threatening illnesses, the Investigational Review Board (IRB) must approve a series of supplementary documents.
- Medical device trials generally receive approval in Korea within 30 days.
Clinical Trials for Pharmaceuticals in Korea
- Companies must go through the Clinical Trial Authorization (CTA) process.
- Before beginning the pharmaceutical clinical trial in Korea, applicants must choose trial sites and a Principal Investigator (PI).
- Korean PIs must be well educated, trained, and have foreign language abilities.
- The sponsor and head of the clinical trial site will sign a written contract before the trial begins.
- If a CRO is used, the sponsor must write a contract outlining a set of tasks for the CRO to complete.
Local Representative
To obtain approval of a clinical trial protocol in South Korea, a foreign company without an established presence in Korea must delegate all rights and responsibilities for the execution of the clinical trial through an agreement with a contract research organization (CRO) established in Korea.
Do you have any queries or looking for regulatory support in various stages of drug development? talk to us at [email protected] or provide your query details in the below form
Electronic Filing System (KiFDA)
Korea’s drug clinical trial approval forms can now be submitted through the e-registration system. Applicants and CROs can self-register their products after receiving approval.
CRIS (Clinical Research Information Services)
- The South Korean government developed a web-based platform called CRIS (Clinical Research Information Services) to facilitate the management of clinical trial information..
- It is a central database that provides information on ongoing clinical trials conducted in South Korea.
- The CRIS includes any clinical trial or research which will prospectively conduct with human participants, aiming to prevent, detect, diagnose, or treat diseases.
- The IRB should approve the clinical trial before registering it on the CRIS.
- The Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC), with support from the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW), established the CRIS.
- It joined the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) as an 11th member of the Primary Registry.
Parallel approval process
In South Korea, the application process for both CTA and IRB is parallel.
Step by step clinical trial approval process in South Korea
The clinical trial approval process in South Korea involves several steps, which include:
- Submission of the clinical trial application: The first step in the approval process is to submit a clinical trial application to the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). The application should include details of the trial protocol, including the study design, objectives, inclusion/exclusion criteria, and endpoints.
- Ethical review: The Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) forwards the application to the Institutional Review Board (IRB) for ethical review once they receive it. The IRB is responsible for reviewing the study protocol to ensure that it meets ethical standards and protects the rights and welfare of study participants.
- Regulatory review: After receiving ethical approval, the MFDS conducts a regulatory review of the clinical trial application. The regulatory review includes an assessment of the scientific validity of the study, as well as a review of the safety and efficacy data.
- Approval decision: Once the regulatory review is complete, the MFDS makes a decision on whether to approve the clinical trial application. If the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) approves the application, the sponsor may proceed with the trial.
- Post-approval reporting: After approval, sponsors must submit regular reports on the progress of the trial to the MFDS. This includes safety reports, interim analysis reports, and final study reports.
Time of approval
The process for regulatory approval takes about 30 days and for IRB, it takes about 50 days.
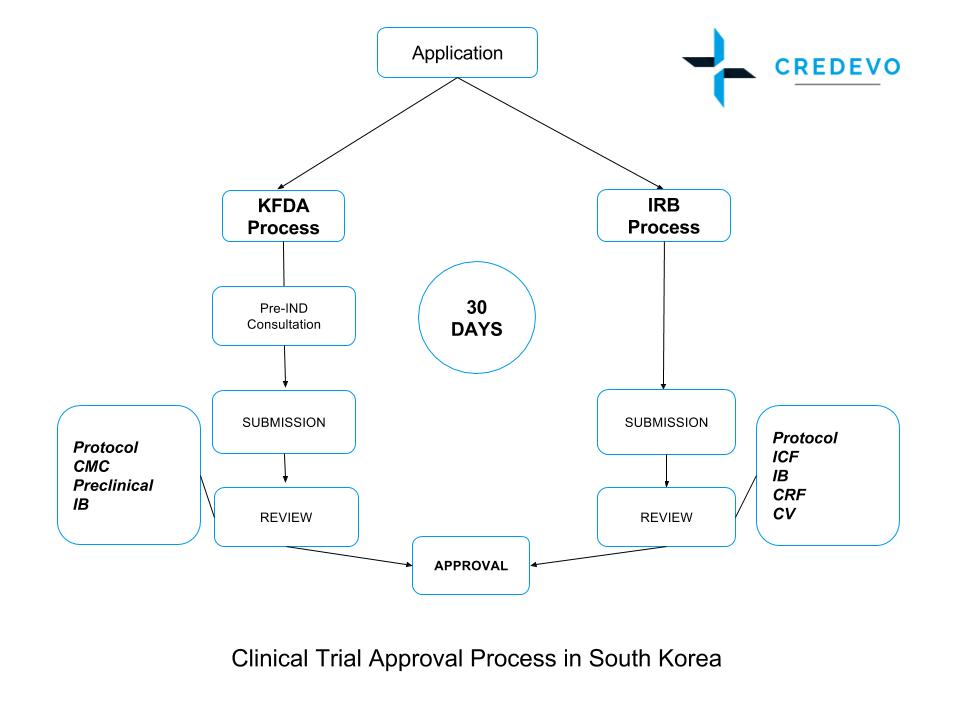
Legends: ICF-informed Consent Form; IB-investigator Brochure; CRF-case Report Form; CMC-chemistry, Manufacturing, And Controls
Guidelines for clinical trial approval (CTA) for drugs
See the guideline here
Documents required for clinical trial approval
- Development Plan
- Introduction
- Data on the evidence of chemical structure and the physicochemical and biological properties (including a placebo)
- Non-clinical tests
- Clinical trial
- Clinical trial protocol
- Investigator’s Brochure
Exemption from submission of data for the category of drugs below
KFDA provides some exemptions for the submission of data for some categories of drugs as below
- A drug is under development in Korea for the first time in the world.
- A drug is under development in any foreign country.
- Prior consultation with the Commissioner of KFDA as provided in Article 14, and acknowledgment of appropriateness, allows the applicant to apply for Clinical Study Authorization.
- This applies to clinical trials conducted for meeting permit conditions after the drug’s license is issued.
- An orphan drug.
- A drug with adequate clinical evidence in Korea and foreign countries, if the applicant plans to begin a confirmatory clinical trial associated with licensing the drug, including any amendments.
- A new drug made from natural substances, excluding cases where any characteristic component is separated and extracted, is the subject of reference.
- A new drug with a component(s) used in Korea before but with different indications, usage, posology, method of administration, composition, formulation, and/or administration route, and safe to use.
- The Commissioner of KFDA separately acknowledges other drugs.
Import of investigational medicines
- Before shipping the investigational product into Korea, the sponsor needs to obtain an import permit.
- After clinical trial application approval, the Korea Pharmaceutical Traders Association (KPTA) authorized by the MFDS, issues the permit for imported pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and herbal medicines.
- The process uses the Electronic Data Interchange of the Korea Customs Service.
Procedural requirements
Clinical trials must be conducted following the standards under the Good Clinical Practices for pharmaceutical products and medical devices.
Are you looking for clinical trial regulatory support
Talk to us today. Provide details of your requirements and we will connect with you.
One thought on “South Korea – Clinical Trials Regulatory Process”
Comments are closed.