Clinical Trials in Taiwan – Part 2: Regulatory

Taiwan is emerging as a big player in the Asian clinical trial market. Taiwan has many advantages for conducting clinical trials. Refer to Part 1 of this blog for more details.

In this part, let’s talk a bit about the clinical trial regulatory scenario in Taiwan, including the approvals required and how to be prepared for it.
Top 6 advantages of conducting clinical trials in Taiwan
There are many advantages for conducting clinical trials in Taiwan, and here are a few of them
- World-class, high-quality infrastructure
- Low trial conducting cost
- Easy patient recruitment process due to dense population
- Fast ethical and regulatory submissions
- Internationally trained healthcare personnel with fluency in both English and Chinese
- Clinical trials comply with ICH-GCP standards
Clinical trial approval
The Taiwan Food and Drug Administration (TFDA) with assistance from the Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE), handles applications of new drugs, medical devices, and clinical trials to fulfill regulatory requirements in line with international norms.
Most of the essential documents, including the Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) section of investigational new drugs (INDs) and new drug applications (NDAs), for clinical trial approval, can be in English.
The current process to apply and secure approval process is as follows
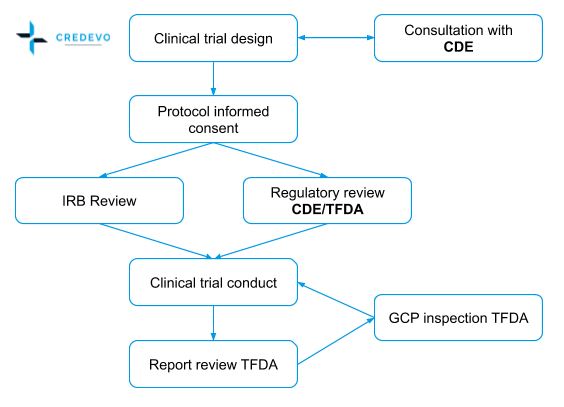
The approval process of a clinical trial in Taiwan
Figure 1. The clinical trial approval process in Taiwan (Adapted from http://www.taiwanclinicaltrials.tw/why1.php)
Need support for your clinical trials in Taiwan?
Credevo provides a wide range of innovative development strategies, clinical trial monitoring services, country-level, and site-level feasibility studies, global regulatory support worldwide for all your products, ranging from simple to complex ones. Complete the form below to connect with us and explore our services.
Many applicants report that, for a general (not US-FDA submitted) clinical trial, it takes about 3 months for Taiwan FDA to give their approval. For clinical trials, approved by USFDA, approvals are quite faster (about 15 days), as discussed later in this article.
The TFDA issues an import permit for the import of drugs used in clinical trials. Customs will allow investigational product import into Taiwan as per the quantity on the import permit.
Innovative IRB Collaboration System (cIRB) for Multi-center Clinical Trial
- In 2013, under the authorization of MOHW, a centralized institutional review board system (cIRB) was set up by CDE and this is to improve the efficiency of case review processes.
- The cIRB comprises 9 main IRBs and 21 collaborative IRBs.
- Currently, 23 IRBs are certified by SIDCER/FERCAP (Strategic Initiative for Developing Capacity in Ethical Review/Forum for Ethical Review Committees in the Asian and Western Pacific Region), and 6 sites are accredited to AAHRPP (Association for the Accreditation of Human Research Protection Programs Inc).
- The main IRBs complete the review process within 20 days whereas the collaborative IRBs complete it within 10 days, but practically, it takes about 1 month or more in the former cases.
- However, USFDA approved trials take less time for approval.
The proven efficiency of cIRB
- The collaborative reduced duplication of the full-review board by 71.3%
- This also reduces the use of IRB resources and shortens the time investigators spend obtaining approval from IRBs at all participating sites
Innovative IRB Collaboration System (cIRB) for Multi-center Clinical Trial (from 2013)
- 462 multicentre trials using the system
- Out of which, 377 trials underwent the main review process
- Average of 9.9 days for the main review process
- 1195 subsequent expedited reviews
- Average of 8 days for the expedited review process
- 96.6% of cIRB got review results by 20 working days
cIRB Approval Process for Multi-Center Clinical Trials
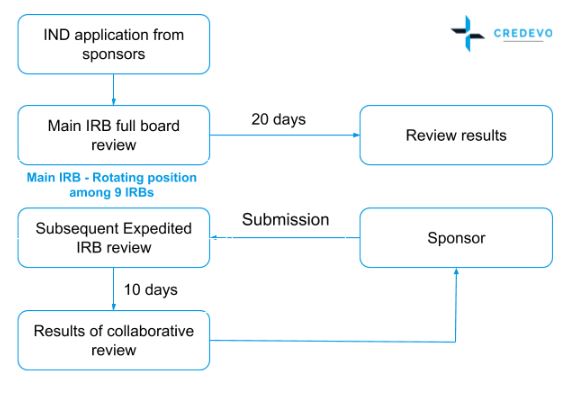
- A multi-site study needs to register with the cIRB system
- The main IRB conducts a full board review and completes it in 20 days.
- The review records and results are then sent to other IRBs in all participating sites
- These IRBs conducts an expedited based review which completes in 10 days
Figure 2. Innovative cIRB system for multi-centered clinical trials in Taiwan (Adapted from http://www.taiwanclinicaltrials.tw/why1.php)
- TFDA has developed a fast track system for clinical trials in Taiwan as part of a global multiregional clinical trial (MRCT), to expedite patient access to new drugs. This is referred to as a Multinational CT notification (CTN) Scheme.
- By this process, the overall review time can be reduced to 14 days by a fast track review, if the sponsor submits the protocol simultaneously to the US FDA and/or European Medicines Agency.
Risk management of clinical trials in Taiwan
For better risk management, TFDA classifies the risks as below
Risk-based IND review tracks
Lowest risk IND
- Fast track (U.S, FDA approved IND)
- Clinical Trial Notification (CTN)
Intermediate risk IND
- TFDA/CDE review team only with or without consulting AC members
Hight risk IND
After review of TFDA/CDE review team – call an advisory committee for final decision
Multinational CT Notification (CTN) scheme
- MRCT protocol approved by one of the 10 referenced countries: USA, UK, France, Japan, Switzerland, Canada, Australia, Sweden.
- At least one medical Taiwan’s medical center joins the trial together with sites of referenced countries.
- Only administration review by TFDA, no technical evaluation from CDE unless regarded as high risk.
- TFDA reserve the right to mend the trial during trial conduction.
The proven efficiency of CTN
Approvals of CTN are growing as well and accounts for 30% of IND trials
Figure 3. CTN Scheme for multinational clinical trials in Taiwan (Adapted from http://www.taiwanclinicaltrials.tw/why1.php)
- In 2009, a bridging study system was developed to provide clinical data on pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) or clinical data on safety, efficacy, dosage, and dose regimen, which will allow extrapolation of the foreign clinical data to different populations. This can greatly help to bring foreign conducted study results to Taiwan. See the details here!
Taiwan: Gate to china clinical trial market
In 2010, the Cross-strait Medicine and Health Cooperation Framework Agreement was signed between Taiwan and China to facilitate the exchange of information in areas of healthcare and clinical research.
The signing of this agreement has resulted in the acceleration of the drug approval process allowing more drugs developed in Taiwan to enter the Chinese market.
Under this agreement, four Taiwanese hospitals are
- Taiwan Taipei Veterans General Hospital,
- Tri-Service General Hospital,
- Taiwan University Medical College Affiliated Hospital, and
- Linkou Chang Gung Memorial Hospital
and are now recognized as clinical trial canters by China. Similarly, clinical data from
- Peking Union Medical College Hospital,
- Peking University First Hospital,
- Shanghai Zhongshan Hospital, and
- Shanghai Ruijin Hospital, in China,
can be used to apply for an NDA in Taiwan.
The new policy has encouraged multinational companies to carry out clinical trials in Taiwan as the cross-strait agreement and this not only reduces the number of overlapping trials in Taiwan and China but considerably shortens the timeline for getting new drugs into the market.
Summary
Taiwan is emerging as a big player in the Asian clinical trial market.
- Strong medical infrastructure including the center of excellence with ICH-GCP compliance
- Government support for 6 Phase I centers
- Renown international medical technology
- Global top 200 hospitals in Taiwan accounted for 14 after the United States, and Germany ranked 3rd in the world, and first in Asia
- Infant mortality rate 4.4/1000 persons (USA infant mortality rates is 5.96/1000 persons)
- Accredited and adequately operated IRB
- 6 AAHRPP accredited
- Innovative cIRB (IRB collaboration system) for multicenter clinical trials since 2013.
- 96.6% of cIRB submissions get review results by 20 working days.
- Well-organized TCTC (Taiwan Clinical Trial Consortium) in 13 specific therapeutic areas.
- Proven track record in producing reliable and high-quality data.
- Experienced clinical research investigators and nurses.
- Efficient and transparent regulatory review system (standard and CTN) for IND.
- Conducting a clinical trial in Taiwan may gain a higher reimbursement price.
- Bridge to china.
Summary: Taiwan Clinical Research Facts (Adapted from http://www.taiwanclinicaltrials.tw/why1.php)
Need more info or Support?
Feel free to contact us with your questions or if you need any support in Taiwan.
References
- http://www.fda.gov.tw/upload/133/Content/2014033109035995639.pdf
- http://tc2.ntu.edu.tw/en/
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results/map?term=multinational+trials&map=ES
- SIDCER Recognition Programme. http://www.sidcer.org/new_web/index.php?group=main&open=recognition.php
- AAHRPP Accredited Organizations. http://www.aahrpp.org/learn/find-an-accredited-organization
- Yang Y-T, Huang H-W, Chen Y-T, et al. Regulation of new drug approval in Taiwan. Ther Innovation Regulatory Sci 2016; 50:602-608.
Disclaimer: Information provided in this blog is not being claimed as official. Applicant is strongly advised to check the recent requirements with relevant authorities.
One thought on “Clinical Trials in Taiwan – Part 2: Regulatory”
Comments are closed.