Ovarian Cancer: Clinical Trial Feasibility
With patients with ovarian cancer as the target trial population, clinical trial feasibility was performed. The clinical trial sites/investigators, who participated in this feasibility came mainly from India, Russia, the Philippines, Vietnam, Thailand, and South Korea.
What are the causes of ovarian cancer?
The causes of ovarian cancer are unclear but doctors have identified factors that can increase the risk of the disease.
- Cancer begins when a cell develops mutational errors in its DNA.
- The mutations tell the cell to grow and multiply quickly, creating a mass (tumor) of abnormal cells.
- The abnormal cells continue living when healthy cells would die. They can invade nearby tissues and break off from an initial tumor to spread elsewhere in the body called metastasize.
Prevalence of ovarian cancer
Age
The risk of developing ovarian cancer gets higher with age. Ovarian cancer is rare in women younger than 40. Most ovarian cancers develop after menopause. More than half of all ovarian cancers are found in women 63 years of age or older.
Overweight or obese
Obese women with a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 probably have a higher risk of developing ovarian cancer, but not necessarily the most aggressive types, such as high-grade serous cancers.
Estrogen hormone replacement therapy
Its thought that women using estrogens alone or in combination with progesterone after menopause have an increased risk of developing ovarian cancer compared to women who have never used hormones.
Having a family history of ovarian cancer, breast cancer, or colorectal cancer
A family history of some other types of cancer such as colorectal and breast cancer is linked to an increased risk of ovarian cancer.
These cancers can be caused by an inherited mutation (change) in certain genes that cause a family cancer syndrome that increases the risk of ovarian cancer.
Prevalence of ovarian cancer
- Ovarian cancer (OC) accounts for an estimated 239,000 new cases and 152,000 deaths worldwide annually.
- Ovarian cancer ranks fifth in cancer deaths among women, accounting for more deaths than any other cancer of the female reproductive system and the tenth most common in China.
- The highest rates (11.4 per 100,000 and 6.0 per 100,000, respectively) are seen in Eastern and Central Europe.
- About 21,750 women will receive a new diagnosis of ovarian cancer and about 13,940 women will die from ovarian cancer.
- A woman’s risk of getting ovarian cancer is about 1 in 78 during her lifetime.
Ovarian cancer clinical trials
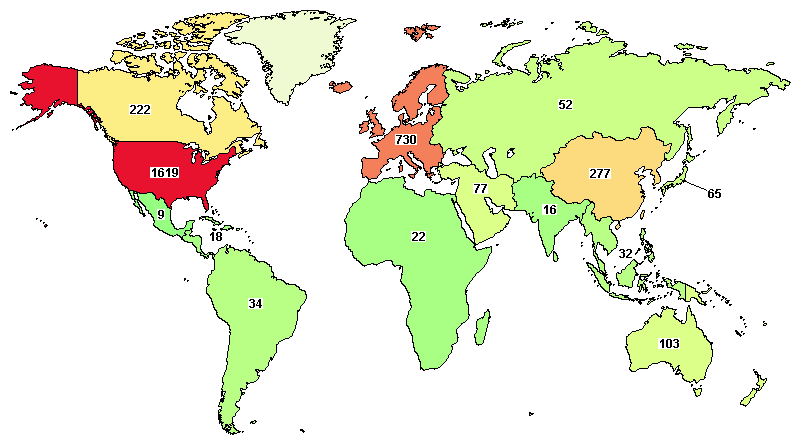
Total clinical trials going around the globe on ovarian cancer are 2,695, where major trials are going in the United States (1,619), UK (215), Canada (222), France (213), and Spain (160).
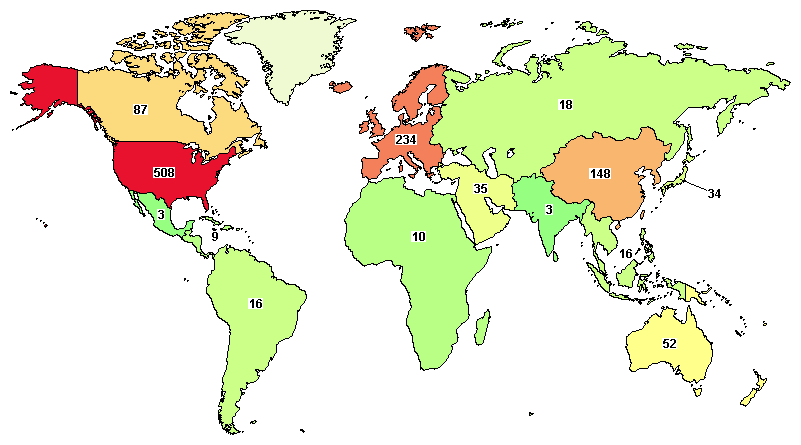
The total ongoing trials on ovarian cancer are 833, where major clinical studies are in the United States (508), France (93), UK (64), China (87), and Canada (87).
Clinical trial details
- The patient population included Ovarian cancer patients, whose disease has progressed or recurred after platinum-based chemotherapy and who are already receiving or scheduled to start therapy with Doxorubicin pegylated liposome intravenous injection
- Patients who have a prior doxorubicin exposure that would result in a total lifetime exposure of 550 mg/ m2 or more after four cycles of treatment were excluded.
- The trial design could be tailored without significant changes to meet USFDA guidance on Doxorubicin Liposome Injection In Vivo Bioequivalence Study.
- While the trial design suits USFDA submission requirements more closely, it could be utilized to target European / Thailand / India / other Asian countries with suitable modifications.
Feasibility results
While clinical trial feasibility was primarily assessed with sites/investigators from India, an attempt was made to get feedback from sites/investigators from other potentially capable regions/countries. Here are the results of this feasibility.
| Country | Avg. recruitment per site per month |
| India | -3 |
| Philippines | 4 |
| Thailand | 1 |
| Vietnam | 4 |
| South Korea | 2 |
| Russia | 4 |
Contact Investigators From This Feasibility Assessment
Would you like to contact these investigators and assess feasibility with them for your clinical trial?
Just provide your email below and further details will be sent to you. Don’t worry, your email will not be published or shared.