Clinical Data Management: Top 5 Important Aspects

Drug developers should ensure that the data submitted to regulatory bodies is definitive from an ethical point of view. It helps to make efficient treatment decisions and ultimately affects patient health. For this, the quality of clinical trial data is crucial. To achieve this quality data, researchers need to have proper data management in clinical trials using clinical data management platforms.
Note: The information in this article was last updated in September, 2022.

Clinical Data Management System (CDMS) has become essential to handle a large amount of data, particularly in multi-center trials. The Clinical Data Management process needs to start early, even before finalizing the study protocol, to obtain an efficient clinical trial outcome. For this, you need to consider several aspects of CDM.
What are the top 5 aspects of Clinical Data Management (CDM)?
The top five aspects of Clinical Data Management (CDM) are
- Key team members
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) in Data Management
- Clinical Data Management (CDM) process
- Data Validation Plan (DVP)
- Discrepancy Management (DM)
- Medical Coding
- Quality
- QA (Quality Assurance)
- QC (Quality Control)
Along with these above aspects, some others include
- Electronic Data Capture (EDC)
- Locking
- Data Entry
Each aspect is crucial for an efficient CDM, So let’s discuss each aspect in detail to understand clinical data management.
Need digital support for your clinical trials?
Do you have any queries or requirements related to Clinical Data Management (CDM) & Biostatistics? Credevo has the expertise to guide you in every stage of drug development. Complete the form below to connect with us to explore our services.
Key team members and their responsibilities for data management in clinical trials
In order to achieve efficient data management, you need to have the following key members as below to drive each function systematically.
- Data Manager
- Database Administrator
- Developer/Programmer (Database)
- Clinical Data Associate
- Quality Assurance Associate
- Medical Coding Associate
Let’s understand each team member’s roles and responsibilities.
Data Manager
- A data manager is a person who is responsible for administering the whole CDM process and preparing the Data Management Platform (DMP).
- He also performs the approval of CDM procedures and all internal documents for data management.
Database Administrator
The database administrator is the one who works upon the software databases in order to find ways to store, manage, organize, troubleshoot, keep databases up to date, and manage clinical trial data.
Database Developer/Programmer
- The database developer/programmer is the one who performs the Case Report Form (CRF) annotation, creates the study database, and programs the edit checks for data validation.
- He is also responsible for designing the data entry screens in the database and validate the edit checks with dummy data.
Clinical Data Associate
- The Clinical Data Associate (CDA) or Clinical Data Coordinator (CDC) designs the Case-Report Form (CRF), prepares instructions for CRF filling, develops the Data Validation Plan (DVP), and also manages the discrepancy.
- The CDA also prepares the CDM-related documents, checklists, and guideline documents.
Quality Assurance Associate
- The quality control associate checks the accuracy of data entry and conducts data audits. However, sometimes, there is a separate quality assurance person to conduct an audit on the entered data.
- Additionally, the quality control associate verifies the procedure documents that need to follow.
- The data entry personnel will track the receipt of CRF pages and performs data entry into the database.
Medical Coding Associate
- The medical coder assigns codes to diagnoses and procedures using ICD (International Classification of Diseases), CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) codes, or other similar platforms.
- The medical coder will do coding for adverse events, medical history, co-illnesses, and concomitant medication administered during the study in data management.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) for data management in clinical trials
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are uniformly written procedures, which contain instructions to record routine operations, processes, and practices that one need to follow in a clinical trial.
- These SOPs play an integral part in clinical research and help to handle the standard practices and daily processes to execute the research tasks concerning institutional, federal, and state guidelines.
- The SOPs should contain adequate detail to guide the research staff through a particular procedure, and thereby it helps to establish uniformity in the everyday functions of the department. Each SOP will have a specific aim.
The key elements of an SOP include
- The objectives of the SOP,
- Definitions of significant terms and acronyms,
- Defines the list of responsible individuals and
- Details that outline the procedures with attachments of examples wherever applicable or necessary.
The common type of SOPs in clinical trials include
- Form Design (Paper-based CRF)
- Database Design (Paper-based CRF)
- Form and Database Testing
- Data Validation Plan
- Writing CRF Completion Guidelines
- Double Data Entry Application Development
- CRF/DCF Tracking
- Double Data Entry Application
- Entry and verification of data
- Data Validation and Cleaning
- Data Management Report
- Backup Schedules and Policies
- Disaster Recovery Plan
- Database Lock & unlock
- Project Change Request
- Archiving
Process for data management in clinical trials
- The clinical data management process generally starts with a plan to create a protocol, approve and sign the relevant document.
- Now moving forward with the next step, design/development is the second and most crucial step, as it incorporates setup of the database, form design, edit checks, validation, etc.
- Then comes the next step, the data management, and review. This step involves analysis, statistical planning, programming, and medical writing.
- The final step of CDM consists of filing, submission coordination, QA, review, and create a submission for the regulatory authority.
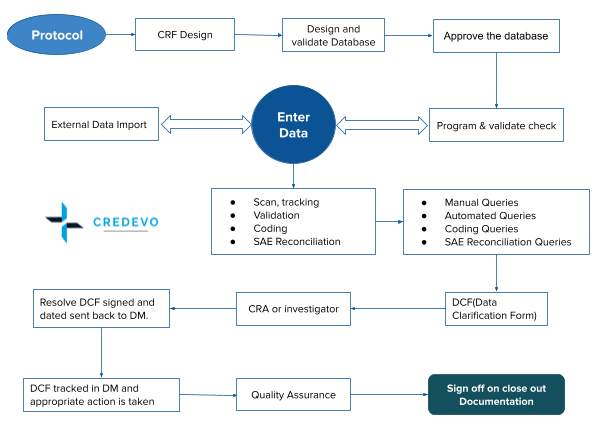
Data validation
- If the data from clinical trials is entered wrongly into the system, it creates a big downstream while reporting. And, the unstructured data, even if entered correctly, will incur costs to clean, transform, and store.
- Therefore, it is necessary to ensure that the data which enters the system is correct and meets the desired quality standards. Hence, to avoid such data inconsistencies, data validation becomes necessary.
- Data validation refers to the process which ensures the accuracy and quality of data. It is implemented by building several checks into a system or report to ensure the logical consistency of input and stored data.
Discrepancy management
Discrepancy management (DM) is also known as query resolution. DM is the process that systematically addresses discrepancies generated within a study.
The DM includes
- Review discrepancies,
- Investigate the reason, and
- Resolve them with documentary proof or declare them as unresolvable.
DM helps to clean the data and gather enough evidence for the deviations seen in the data. All Clinical Data Management Systems (CDMS) will have a discrepancy database in order to record and store all the discrepancies with an audit trail.
Medical coding
- Medical coding is somewhat like translation. Here the coders obtain medical reports from clinical investigators, which may include patient condition, the doctor’s diagnosis, a prescription, and whatever procedures the doctor or clinical investigators perform on the patient, and turn that into a set of codes, which make up a crucial part of the clinical trial.
- Coding helps classify reported medical terms on the Case Report Form to standard dictionary terms in order to achieve data consistency and avoid unnecessary duplication in clinical trials.
- For the classification of events, coders generally use medical dictionaries available online. Coders use Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) for the coding of adverse events as well as other illnesses, and World Health Organization-Drug Dictionary Enhanced (WHO-DDE) for coding the medications.
Quality in clinical data management
One can maintain the quality of clinical trial data through inspection, evaluation, and standardization by using various tools and processes. The two crucial steps to manage data quality are quality assurance and quality control, known usually as QA and QC.
Quality Assurance
- Quality Assurance in data management is a continual and dynamic practice process to prevent mistakes and defects while creating data. It helps to ensure that the clinical research conducted and data generated complies with the regulatory standards.
- QA is a crucial activity required throughout the clinical research process to ensure the high quality and integrity of data. The QA process starts with examining the patient requirements and is involved in every step until the final performance qualification wherein the test results are compared to the user requirements.
The QA applies for following aspects
- Generation, record, analysis, and reporting of the clinical data follow the protocol, Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and Good Clinical Practices (GCPs).
- Identify and correct data processing errors, and provide feedback to data managers and research staff during and after completion of a study.
- Report any special data processing situations or deviations from coding conventions.
- Inspection of the tasks, task-execution by clinical researchers, and documents of the clinical research.
- Determine conformity of the actual conditions with the specified requirements.
- Ensure the protection of rights and safety of the trial subjects.
- Examine the resultant clinical data for its correctness.
- Determine whether the operations performed are compliant with the federal and state environmental protection laws and regulations.
Quality Assurance in CDM has numerous benefits and a few of them include
- Improves reliability of results
- Enhance accuracy and consistency through audits
- Identifies and troubleshoots the ambiguities
- Adherence to compliance
Activities in QA involves
- Computer System Validation (CSV): Computer systems validation examines all aspects of the data handling of computer systems (hardware and software) to ensure the accuracy, reliability, consistent performance, and the ability to discern invalid or altered records.
- The validation process begins with the system proposal and continues until system retirement and e-records retention based on regulatory rules.
The validation process includes the following
- Validation planning
- User specification
- Detailed design & timelines
- Configuration & coding
- Reporting release
- OQ – Operational Qualification
- IQ – Intelligence Qualification
Quality Control
In clinical research, the quality control process assures internal consistency through periodic operational checks at every stage of the trial process and data handling to verify the compliance of the trial process and reliability of the data.
Data Management Plan (DMP)
The Data Management Plan is a written document, and it contains the details of the plans for the collection and management of data throughout the clinical trial lifecycle.
For productive data management, planning must begin at the time of trial design. The Data Management Plan is a part of quality control and process management in clinical trials.
- DMP should consider the collection and management of data during the trial, data sharing, and archiving at trial closure.
- The data manager ensures to carry out all tasks and procedures detailed in this plan.
- A DMP for a trial must be ready before the start of data collection. So that this will ensure that the data is in the correct format, organized, and annotated appropriately.
- A well-designed Data Management Plan will provide a road map to handle the data, establish processes to handle unforeseeable conditions, and assess potential risks.
- The ideal result is to provide a database that is accurate, reliable, secure, and ready for analysis.
Final validation of the data is carried out after entering all data into the data management plan, and this is to ensure the validity and reliability of the data.
Here are few recommendations to develop a DMP
- A draft of DMP must be available before the enrolment of the first trial participant.
- The DMP must be written in compliance with applicable regulatory requirements, oversight committees and relevant Standard Operating Procedures (SOP).
- DMP must clearly identify the roles and responsibilities of the data management group/team.
- Data management processes must be clearly defined from trial initiation to database lock.
- Data archiving and data sharing should also be documented in the DMP.
Some other aspects of clinical data management are
Electronic Data Capture
Electronic Data Capture (EDC) is a computerized system designed to collect clinical data in electronic format. EDC replaces the traditional paper-based data collection method to streamline data collection and expedite the time to market for drugs and medical devices.
The EDC system provides
- A GUI (graphical user interface) component for data entry.
- Validation component to check user data.
- Helps as a reporting tool for collected data analysis.
- Can increase data accuracy and decrease the time to collect data for studies of drug and medical devices.
Click here for more information about Electronic Data Capture (EDC)
Locking
- The database lock system is a complete process, but a necessary industry standard. The locking function secures the data and ensures its quality by preventing further editing prior to submission to FDA.
- After the final quality check and data validation, the formatting process leads to a delay after the lock. The EDC support partner that helps ensure data maintenance and validation throughout the study changes the outcome of database lock.
- The goal is to limit the changes made to data and keep the database clean.
- After obtaining the approval for locking from all stakeholders, the database is locked to extract the clean data for statistical analysis. Generally, modification in the database at this stage is not possible. But in case of a critical issue or other crucial operational reasons, privileged users can modify the data even after the database is locked.
Data Entry
- Data entry refers to various modes of entering information into a computer for further processing. It may be the direct computer entry that can be by a person transferring data from paper-based CRFs into a computer database.
- Understanding all these important aspects of data management in a clinical trial, you need to identify an efficient clinical data management platform.
Are you looking for effective clinical data management & biostatistic solutions for your clinical trial?
Talk to us today. Provide preliminary details below, and we will help you achieve your clinical data management objectives for clinical trials.