Cosmetics Registration Process In Japan

Japan is one of the world’s leading cosmetic and personal care products (beauty products) markets. The experts assume the beauty and personal care products market to grow at a CAGR of 3.5% over the next five years. Cosmetics shipments within Japan generate a market value of around 2.7 trillion Japanese yen. Due to this market size, many global manufacturers show interest in marketing their products in Japan.
Note: This information was last updated in September, 2022.

Top reasons to choose Japan market for your cosmetic products
- Constant cosmetics market growth.
- Highly popular in Asia, accounting for 90% of Japanese exports.
- Have the highest per person expenditure on cosmetics & skincare products.
- Increase in demand for natural & organic beauty products.
- The rich culture and their obsession for beauty.
- Increasing demand for denture products with the increasing aging population.
Regulatory authority for cosmetics in Japan
- In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare (MHLW) under the Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Law regulates cosmetics. A series of subsidiary rules, standards, and guidance documents issued by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare (MHLW) support cosmetics.
- The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) conducts on-site along with document-based inspections to evaluate the adverse effect reports and review the applications of foreign manufacturers and importers.
- Pharmaceutical Affairs and Food Sanitation Council is MHLW’s backup expert panel.
- Prefectural governments are responsible for licensing, inspection, and guidance.
Types of Cosmetics in Japan
Japan regulatory classifies cosmetics broadly into two types
- Cosmetics, and
- Quasi-drugs
Cosmetics
Cosmetics are products that have mild action on the human body and are applied by rubbing, sprinkling, or other methods, which aim to clean, beautify and increase attractiveness, alter the appearance, or keep the skin or hair in good condition.
In the Japanese market, six different categories of cosmetics are
- Perfume and eau de cologne: Perfume and eau de cologne
- Makeup cosmetics: Foundation creams, lipsticks, eye makeup, and others
- Skincare cosmetics: Skin lotion, essence, skin milk, cleansing cream, and others
- Haircare products: Hair dye, shampoo, hair treatment, and others
- Special-purpose cosmetics: Sunscreen, shaving cream, and others
- Cosmetic soaps: Soaps for cosmetics
Quasi-drugs
The quasi-drugs products have mild effects on the human body, and the MHLW designates based on the characteristics.
Generally, quasi-drugs include
- deodorants,
- depilatories,
- hair growth treatments,
- hair dyes,
- bath products,
- dentifrice,
- perm, and
- straightening products and
- medicated cosmetics.
The cosmetic products that come under quasi-drugs include
- Whitening products
- Anti-aging products
- Oily skin or acne treatment products
- Anti-dandruff or anti-itching products
- Freckle-removing products
- Shaving products
- Anti-sunburn or “snow burn” products
- Anti-bactericide products
The difference between cosmetics and quasi-drugs is not clear. However, the distinction is differences in the effects of the product, nature, the number of ingredients used, the application method, and the product appearance.
Cosmetics and quasi-drug ingredients should comply with Cosmetics and Japanese Standards of Quasi-drug Ingredients. The regulations governing each category differ slightly, and the requirements for quasi-drugs are more strict.
The application procedures of marketing and manufacturing licenses for quasi-drugs are similar to cosmetics. But the requirements for quasi-drugs are more strict.
Need support for your cosmetic products market approval in Japan?
Credevo offers expertise in medicines, cosmetics, nutraceuticals (Health Foods) registrations, clinical trial regulations, and many more services in Japan. Check them out now!
Let’s see how you can market each category of cosmetics in Japan.
How to get the market approval of cosmetics in Japan?
To market the beauty products in Japan, one needs to know answers to the following questions
- How are cosmetics regulated in Japan?
- What are the regulatory requirements and processes for different categories of cosmetic products?
- What are various licenses required for marketing?
- How do foreign manufacturers market their cosmetic products in Japan?
- How to import cosmetic products after obtaining the required approvals?
Let’s see how you can market your cosmetic product in Japan stepwise.
Step 1: Review, categorize and perform ingredient analysis for your product.
The application process for marketing and manufacturing licenses for quasi-drugs is the same as for cosmetics. However the requirements and regulators vary. Regulators inspect Quasi-drugs more keenly for safety.
The requirements and regulations vary between the category of the product. As a result before initiating any registration process, you should review and find your product category first.
The next step is to conduct ingredient analysis on samples by testing at the facilities designated by the MHLW, owned or contracted by manufacturers/importers. It includes analyzing the list of ingredients and whether it complies with Japanese standards for cosmetics. However, this is not a mandatory process, but authorities may ask for these reports during the inspection.
Step 2: Obtaining Required Licenses.
The next step is obtaining the required licenses such as Cosmetic Manufacturing License and Cosmetic Marketing License from the respective regulatory authorities. The validity of these licenses is 5 years.
Foreign manufacturers, who intend to manufacture quasi-drugs in foreign countries and export them to Japan, should be accredited by the MHLW as an “Accredited Foreign Manufacturer”.
A Japanese marketing license holder who markets quasi-drugs manufactured by a foreign manufacturer can make an accreditation application on the manufacturer’s behalf.
Three categories of accreditation include,
- Accreditation for all or part of the manufacturing process of quasi-drugs and sterile quasi-drugs.
- Accreditation for packaging, labeling, or storage during the manufacturing processes of a quasi-drug.
Marketing License holders have to implement a set of standards called
- Good Quality Practice (GQP) for maintaining the quality of products, and
- Good Vigilance Practice (GVP) for undertaking appropriate actions for safety management.
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice)
PMDA conducts on-site and document-based GMP inspections of domestic and foreign manufacturing sites for high-risk products. The GMP inspection to ascertain whether the manufacturing facilities and manufacturing and quality controls comply with standards such as the Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP).
Step 3: Cosmetic & Quasi-Drug Marketing Notification Submission.
After the manufacturers obtain the license and before initiating the import & selling, they shall submit cosmetic marketing notification to the same authority who issued the cosmetics marketing license.
- Cosmetics Import Notification for Manufacture and Sales
- Cosmetics (foreign manufacturer, importer) notification
Domestic manufacturer needs to submit only Cosmetic market notification to the same regulatory officials as granted the cosmetics marketing license.
Step 4: Import your Cosmetics and Quasi Drugs into Japan.
Importers should implement all the requirements mentioned above with some slight differences. An importer can handle the importation or distribution of its products by opening a local subsidiary. In this case, the local company should follow specific regulations to be an importer.
For the import of cosmetics and quasi-drugs into Japan, you need to obtain
- Primary distribution approval
- Cosmetic Manufacturing License (packaging, labeling, and storage).
In order to obtain the license, the importer needs to built a product safety and quality management system for its company and have to implement a set of standards called Good Quality Practice (GQP) and a Good Vigilance Practice (GVP).
You need to appoint the importer for your products, and ensure that the products are by the law in Japan. This assessment is performed on samples of the products by “testing and inspection facilities” designated by the MHLW.
Labeling & Claims
For Cosmetics
Cosmetic labels need to be in Japanese, and full ingredient labeling in Japanese is mandatory on the outer package of cosmetics. Labeling with misleading expressions and unapproved claims of functionality or efficacy are prohibited.
The Japan Cosmetic Industry Association (JCIA) has compiled a Japanese version of the “List of Cosmetic Ingredient Label Names” to use this in compliance with the PMDL’s requirements to list all ingredient names on the labeling.
Companies can refer to the document to standardize the Japanese name of ingredients. Companies can refer document to standardize the Japanese name of ingredients and file a request with the JCIA to revise a new label name.
Quasi-drugs
For quasi-drugs, a label shall contain the name of specific ingredients prescribed by the MHLW. MHLW doesn’t offer a reference list of permitted or prohibited claims for quasi-drugs. The claim made for quasi-drugs depends on active ingredients. The sponsor can market the product only after approval.
Example: Claim of Whitening efficacy with a product containing the active whitening ingredient, Claim of Anti-acne efficacy with a product containing an anti-acne active ingredient.
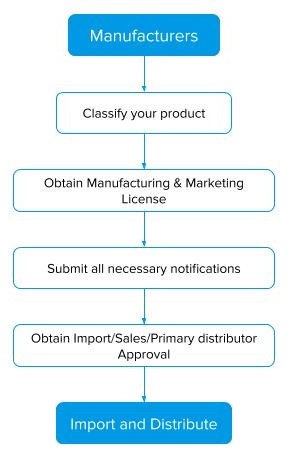
Approval Process for cosmetics and Quasi Drugs
Summary points to market your cosmetics product in Japan.
- Regulations, requirements, and registration processes vary with a product category.
- The cosmetic products shall meet the Japanese law criteria.
- The primary importer will handle most product compliance jobs locally before importing products into Japan.
- The primary importer should acquire a cosmetics manufacturing and sales license.
- The importer needs to implement Good Quality Practice (GQP) and a Good Vigilance Practice (GVP) and undertake appropriate measures for safety management.
- The sponsor needs to assess products at testing and inspection facilities designated by the MHLW.
- An importer needs to submit three forms.
- A Manufacture and Sales of Cosmetics Notification,
- A Cosmetics Import Notification for Manufacture and Sales, and
- The manufacturer’s or importer’s brand name.
Do you need support or have queries on the Cosmetic & Quasi drug market approval process?
Credevo offers a wide range of drug development and regulatory services in Japan. Choose one of the following options to connect with us.
Get the report on the Cosmetic products market approval process in Japan.
Note: This report will be charged @ $1424.
Do you have a query? Just ask experts at Credevo.
Note: “Ask Credevo Expert” will be charged @ $50 / inquiry. Any inquiry requiring more than 30 min of the expert’s time will incur additional charges.
Looking for a quotation? Just provide relevant info and we will send you the details.