Japan Nutraceutical Approval Process

The use of dietary supplements and nutraceutical to lower risks for illness and enhance health has gained popularity in Japan over the past few decades. The shipment value of health foods in Japan reached about 888 billion Japanese yen in the fiscal year 2021, continuing the upward trend from previous years. The market was expected to grow by more than 900 billion yen in the upcoming fiscal year 2021.
(Last updated in August 2022)

The rise in healthcare costs, coupled with the growing geriatric population, is considered the one prominent reason for Japan’s functional food industry’s growth.
The Council of Pharmaceutical Affairs and Food Hygiene under the MHLW scientifically evaluates the food products which come under the FOSHU (one of the categories of health products) for their effectiveness and safety.
After implementing a functional food system, numerous FOSHU products with strong clinical backing and positive health effects were created and released on the market. The shipment value of the foods with function claims market in Japan was estimated to reach around 327.8 billion Japanese yen in the fiscal year 2021, continuing the ongoing upward trend.
Top reasons to choose Japan market for your nutraceutical products
- The positive market growth for nutraceuticals and dietary supplements.
- Easy regulatory process.
- Huge market size.
- Increasing aging populations and an increase in intake of health supplements.
- Gaining awareness of using health products for wellbeing.
- The country’s fast pace and busy lifestyle make its consumers strongly rely on dietary supplements.
Nutraceuticals/health foods navigation in Japan
The food or food ingredients that have defined physiological effects, Europe regulates as ‘nutraceuticals’ or ‘food supplements’ and Australia as ‘complementary medicines
In Japan, the terms “nutraceuticals” or “dietary food supplements are not very popular compared to most other countries and are rather regulated as Foods with Health Claims (FHC).
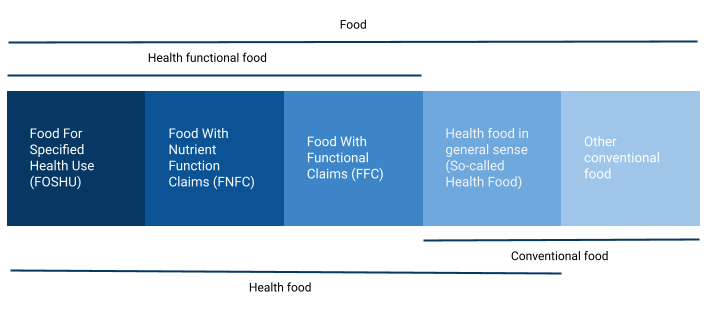
Classification of nutraceuticals in Japan
Regulatory authority for (Health Foods) Nutraceuticals in Japan
The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare (MHLW) is the regulatory authority for Foods with Health Claims (FHC).
The Consumer Affairs Agency (CAA) regulates the advertising and sale of food with health claims. Local health authorities oversee food manufacturing.
The Food Sanitation Act (also known as “FSA”) is the primary law in Japan that controls the integrity and quality of food. The main piece of legislation in charge of regulating food labelling is the Food Labelling Act.
Below table illustrates different foods and concerned authorities
| Laws and Regulations | Responsible organization | Coverage |
| Food Sanitation Act | MHLW/CAA/Prefectural capital | All food and drink, and food-related products |
| Pharmaceutical Affairs Law | MHLW/Prefectural capital/Police | Health food shall not be claimed to have the efficacy of pharmaceutical products |
| Act against Unjustifiable Premiums and Misleading Representations | CAA/Prefectural capital | False and exaggerated advertisements |
| Health Promotion Act | CAA/Prefectural capital | False and exaggerated advertisements (Objects: including media and advertising agency’s improper promotion) |
| Food Labeling Act | CAA/Prefectural capital | Labeling requirements |
Based on the functions and purpose, the Japan regulatory regulates and classifies Health Foods as
- FOSHU – Foods for Special Health Use.
- FNFC – Foods with Nutrient Function Claims.
- FOSDU – Foods for Special Dietary Use.
Foods for Special Health Use (FOSHU)
FOSHU refers to foods containing ingredients with functions for health, physiological functions, and biological activity on the body and is officially approved to claim its physiological effects on the human body.
Based on the application requirements and review process, the FOSHU are classified as
- Ordinary FOSHU,
- Standard FOSHU,
- Re-permitted FOSHU,
- Reduction of disease risk FOSHU, and
- Qualified FOSHU.
Foods with Nutrient Function Claims (FNFC)
Foods with Nutrient Functional Claims (FNFC) refers to foods labeled with the functions of their nutritional ingredients. They are considered to be the “foods with function claims”.
Foods for Special Dietary Use (FOSDU)
Foods for Special Dietary Use (FOSDU) products can use medical and nutritional expressions to indicate that they are appropriate to promote growth or maintain or recover health among infants, children, the infirm, and pregnant women.
How to register your nutraceuticals in Japan?
Japan follows a unique regulatory process. Nutraceuticals are considered Health Foods, categorized, and each category follows a separate regulatory process.
It is crucial to ensure the following points to register nutraceuticals in Japan
- Understand the regulations and various categories of nutraceutical products,
- Review the product details to ascertain the category and regulations that apply for registration,
- Apply with all required documents, respond to queries and receive the product registration, and then
- Import the registered nutraceutical products into Japan.
The process to register health foods/nutraceutical in Japan
Review your product
Before initiating any registration process, one needs to review the product details to ascertain the category to which it belongs and the regulations applicable for registration.
It is better to undertake a detailed and thorough review of regulations for identifying the right category applicable to your product.
Need support for your nutraceutical/health food registration in Japan?
Credevo offers expertise in drug products, nutraceutical/health foods registration, clinical trial regulations, and many more services in Japan. Check them out now!
Submit application with all required details, respond to queries, and receive the product registration
If you are sure of your product category for registration in Japan, and the applicable regulations for your product, gather all the necessary documents. However, it is likely to be driven by the category of the food it belongs to.
You may require the documents that determine the following aspects
- Its effectiveness, based on scientific evidence, which includes clinical studies.
- Its safety as assessed from historical consumption pattern data and additional safety studies conducted in humans, and
- Analytical determination of the functional component responsible for the beneficial physiological action.
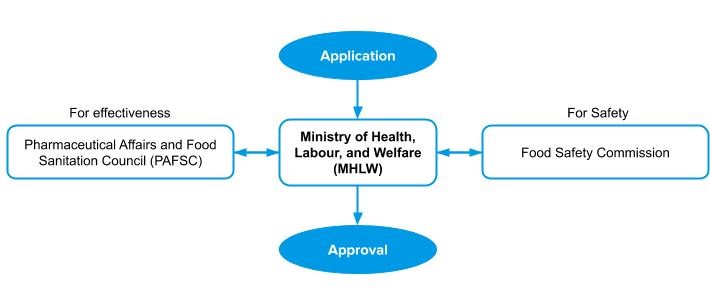
Once you have collected all the necessary documentation, then you are ready for submission. The applicant shall submit the documents to the regulatory authority.
If all the documents are accepted and considered sufficient, then the application will be reviewed by the Pharmaceutical Affairs and Food Sanitation Council (PAFSC) and Food Safety Commission.
The Pharmaceutical Affairs and Food Sanitation Council (PAFSC) and Food Safety Commission check for completeness of the documentation, accepts, and review all the documents.
MHLW sends samples to the National Institute of Health and Nutrition to validate the products’ active ingredients.
The MHLW issues the approval after obtaining the opinion from Pharmaceutical Affairs and Food Sanitation Council (PAFSC) and Food Safety Commission.
Review timeline
Based on the application category, the review timelines may vary.
Approval process flow for nutraceuticals in Japan
Import your nutraceutical products into Japan
After successful approval, the sponsor needs to import the approved products into Japan and for this, the sponsor needs to obtain the import license by submitting the necessary documents to the food sanitation inspection section of the MHLW quarantine stations.
The Japanese legislative framework regulating food imports
- The Food Safety Basic Law
- The Food Sanitation Law
- The Health Promotion Law
- The Japan Agricultural Standards Law
- The Plant Protection Law
- The Domestic Animal Infectious Disease Control Law
- The Food Labeling Law
- The Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Laws
Importers should confirm they appropriately identify their items following Japan’s food and drink product classification, especially whether fresh or raw, as applicable laws vary by product classification. They must also comprehend how important product quality is to the Japanese food and beverage sector.
Conclusion
Japan’s cost of living is generally high and has the highest life expectancy in the world. Their consumption of nutraceuticals shows that older Japanese are willing to pay more for higher quality and nutritious foods. Along with this, the registration process has become faster and affordable than before. Japan’s supportive government and health-conscious consumers are promising factors for nutraceuticals market growth in the future.
Do you need support or have queries on drug/nutraceutical/health food registration in Japan?
Credevo offers a wide range of drug development and regulatory services in Japan. Choose one of the following options to connect with us.
Get the report on Nutraceutical/Health food registration process in Japan.
Note: This report will be charged @ $1424.
Do you have a query? Just ask experts at Credevo.
Note: “Ask Credevo Expert” will be charged @ $50 / inquiry. Any inquiry requiring more than 30 min of the expert’s time will incur additional charges.
Looking for a quotation? Just provide relevant info and we will send you the details.